Avapro
"Cheap 150mg avapro with mastercard, diabetes urine test strips boots."
By: Brent Fulton PhD, MBA
- Associate Adjunct Professor, Health Economics and Policy

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/brent-fulton/
The anopheline species diversity has increased from 2 in the 1930s to 6 in the 1940s to 10 in the 1990s diabetic hhs avapro 300mg amex. A similar situation has occurred in Manaus diabetes signs vision buy avapro 300 mg with amex, where the process of urbanization eliminated An. Nevertheless, the accelerated expansion of the suburbs into the surrounding jungle reestablished the contact between the human population and the principal vector, An. Vectors are also adapting to new circumstances; for example, mosquitoes have varied their feeding time in areas where humans have intervened (Tadei et al. At present, malaria cases continue to be reported from the periurban areas of Manaus. Coastal waters in both industrial and developing countries are frequently contaminated with untreated sewage (see Chapter 19), and warmth encourages microorganism proliferation. Phytoplankton organisms respond rapidly to changes in environmental conditions and are therefore sensitive biological indicators of the combined influences of climate change and soil and water pollution. Algal blooms are associated with several environmental factors, including sunlight, pH, ocean currents, winds, sea surface temperatures, and runoff (which affects nutrient levels), as described in Chapters 12 and 19. Some species of copepod zooplankton apparently provide an additional marine reservoir for V. For example, Nipah virus emerged in Malaysia in 1999, causing over 100 human deaths (Chua et al. This highly pathogenic virus (with a case fatality rate greater than 40 %) was previously unknown as a human pathogen, and emerged from its natural reservoir hosts (fruit bats) via domestic animal (pig) amplifier hosts. First, the virus appears not to be able to move directly from bats to humans, so the development of a pig industry in Malaysia has been a crucial driver of emergence. Second, fruit bat habitat has been largely replaced in peninsular Malaysia by crop plants such as oil palm. These interrelated events are theorized to have coincided just prior to the Nipah virus outbreaks, when the large mid-1990s its long-term persistence in certain regions, such as in the estuaries of the Ganges and Brahmaputra in India. According to this theory, the seasonality of cholera epidemics may be linked to the seasonality of plankton (algal blooms) and the marine food chain. Studies using remote sensing data of chlorophyll-containing phytoplankton have shown a correlation between cholera cases and sea surface temperatures in the Bay of Bengal. Interannual variability in cholera incidence in Bangladesh is also linked to El Nino/South~ ern Oscillation and regional temperature anomalies (Lobitz et al. For instance, expanding ecotourism and forest encroachment have increased opportunities for interactions between wild nonhuman primates and humans in tropical forest habitats, leading to pathogen exchange through various routes of transmission (Wolfe et al. Some 1,415 species of infectious organisms are known to be pathogenic to humans; 61% of these are zoonotic and 75% of those considered as emerging pathogens are zoonotic (Taylor et al. Viruses such as Junin, Machupo, and Guanarito hemorrhagic fever agents in Argentina, Bolivia, and Venezuela, transmitted to humans through the urine of wild rodents, came through the expansion of agricultural practices to new areas; hantaviruses, initially recognized in Korea, came through the urine of infected rodents and were then identified in Asia and Europe. The Junin virus, which causes a hemorrhagic fever, also emerged when the production of vegetables that serve as food source for rodents increased in Argentina in 1957. Because of the key role of zoonoses in current public health threats, wildlife and domestic animals play a key role in the process by providing a ``zoonotic pool' from which previously unknown pathogens may emerge (Daszak et al. The influenza virus is an example, which causes pandemics in humans after periodic exchange of genes between the viruses of wild and domestic birds, pigs, and humans. A number of species are endemic to remote oceanic islands, and these may harbor enzootic and potentially zoonotic pathogens (Daszak et al. The current major infectious disease threats to human health are therefore emerging and reemerging diseases, with a particular emphasis on zoonotic pathogens jumping host from wildlife and domestic animals. This is essentially a process of natural selection in which anthropogenic environmental changes perturb the host-parasite dynamic equilibrium, driving the expansion of those strains suited to the new environmental conditions and driving expansion of others into new host species (Cunningham et al. The selection process acts on the immense pool of varied pathogen strains circulating within the population (c. Even in these examples, it is possible that the new strains were already present in the pathogen population.
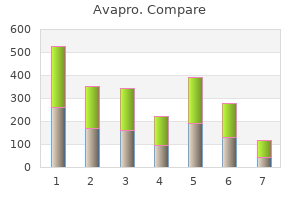
However diabetes symptoms checklist cheap avapro 300 mg without prescription, the sensitivity and specificity of these techniques diabete o que não pode comer safe 150 mg avapro, at least in the case of sonography, appear to be inadequate. The intradermal test shows immediate hypersensitivity and is simple, but it does not indicate if the infection is current. In one study, immunoenzymatic staining and indirect immunofluorescence using frozen sections of the parasite showed sensitivities of 92% and 88%, respectively, and high specificity: 2% false positives with the first technique and 4% with the second (Liu et al. Cross-reactions with cases of acute schistosomiasis, chronic schistosomiasis, and paragonimiasis were observed in 14%, 5%, and 0% of cases using immunoenzymatic staining, and in 14%, 10%, and 0% using indirect immunofluorescence. IgA antibodies were found to have decreased significantly after a month of successful treatment, which indicates that this test can be used to evaluate the results of treatment. Control: the most effective control measure is probably to refrain from eating undercooked fish in endemic areas. Human clonorchiasis does not exist in northern China, where people do not eat raw fish, although it is prevalent in pigs, cats, dogs, and rats in that region. Fish infections can be reduced by allowing human fecal matter to ferment for several weeks before it is used to fertilize fish-culture ponds, as the fermentation process kills C. Treating the population with praziquantel every six months also significantly reduces the passage of eggs into the environment. However, elimination of vegetation from the edges of ponds during the spring and summer will benefit predators that eat snail larvae, which in turn will reduce the population of first intermediate hosts. Viability of metacercariae of Clonorchis sinensis in frozen or salted freshwater fish. Epidemiologic characteristics of Clonorchiasis sinensis in Guandong Province, China. Egg positive rates of Clonorchis sinensis and intestinal helminths among residents in Kagye-ri, Saengbiryang-myon, Sanchong-gun, Kyongsangnam-do. The ultrasound survey of gallstone diseases of patients infected with Clonorchis sinensis in southern Taiwan. Image analytical observation on the growth and development of Clonorchis sinensis in rats. Hepatitis B and C virus, Clonorchis sinensis for the risk of liver cancer: A case-control study in Pusan, Korea. They live in the bile ducts of sheep, goats, cattle, and, less frequently, other domestic and wild ruminants. The first is a land snail (38 species, among them Cionella lubrica in North America, Zebrina detrita and Helicella candidula in Europe, and Bradybaena similaris in Malaysia), and the second is an ant (12 species, among them Formica fusca in Germany and North America, F. They are transported by bile and fecal matter to the exterior, where the first intermediate host ingests them. The egg, which is quite resistant to desiccation, releases the miracidium only when it is ingested by a snail. The miracidium forms two generations of sporocysts in the digestive gland of the snail, the second of which produces numerous cercariae, which are expelled from the snail through the respiratory chamber after about three to four months. Each ant may contain between 38 and 76 metacercariae, depending on the species and size of the insect (Schuster, 1991). It will then bite down and suffer a spasm of the jaw musculature, making it impossible for the ant to let go. Thus trapped high on the vegetation, the ant is likely to be eaten by a definitive host. When herbivores consume infected ants while grazing, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and the juvenile parasites travel against the bile flow to the bile ducts. The first intermediate host is a pulmonate land snail of the genus Limicolaria, and the second is an ant of the genus Camponotus, in which the metacercariae develop. The definitive hosts are domestic herbivores (cattle, sheep, goats) and probably also wild ruminants (Frank et al. Prevalence rates of 40% have been reported in domestic animals in France, 80% in Poland, 46% in Switzerland, 100% in Yugoslavia, and 75% in goats in the Russian Federation. In Greece, parasite eggs were found in 2 of 232 dogs, but there is some doubt as to whether these were true D.
300mg avapro sale. 10 Secrets of the Longest Living People with Diabetes Part 2.
The strategy also requires careful evaluation of means toward self-sufficiency in food diabete xilitolo cheap 150mg avapro mastercard. One of the pervasive themes of the Report is the critical role of human resources in the 5 development of Africa diabetes prevention home remedy discount avapro 300 mg with amex. The development of human resources is the subject of Chapter 6: education, training, and health. With respect to education, one basic strategy issue is addressed: how to expand schooling most effectivelv in the face of severe financial constraints. The training discussion covers a wide range of questions: project-related training; expansion of on-the-job training; the need for special attention to management training; and technical assistance. In the discussion of health sector strategies a number of themes receive attention, including: experimentation with low-cost rural health care strategies and their gradual expansion, taking into account administrative and financial constraints; better use of existing resources through improved planning, policy analysis, and managemenit; mobilization of private as well as public energies; rehabilitation of infrastructure and consolidation of existing health systems; and improvingaccesstopotablewater and adequate sanitation. Although expansion of agriculture is necessarilv the centerpiece of any productionoriented strategy, opportunities for increas- tionale for regional economic integration-the goal of the LagosPlan-and the desirability of a positive donor role in support of moves toward closer regional economic cooperation. Policy-related factors receive priority in the Report, because-for many of the countries involved-the prospects for more rapid and sustained economic development are slight without appropriate adjustments. Domestic policies can be altered, although it is recognized that changes of this sort require time and are not easy to achieve. Agriculture, long neglected, could recapture the growth rhythms of the 1960s if the environment were more supportive. Also, some impact of agricultural research should be felt in the next few years; research now under way can yield results by the 1990s. While the focus of the Report is on responses to the economic crisis of the 1980s, certain longer-term problems cannot be ignored. The six children born on average to an African woman during her childbearing years represent the highest total fertility rate in the world. This high fertility, combined with declining mortality, has effects on agriculture, urbanization, and government spending, which are explored in Chapter 8. It is not a permanent course for any country, but one that in Africa generates resources more quickly than any alternative and benefits more people. Without these resources, the foundations of future development cannot be established. The list of what must be done is formidable: administrative services have to be extended to the rural areas to increase social welfare and contribute to the building of a sense of national unity; critically needed social and economic infrastructure must be developed; roads must be built and maintained; suitable schooling must be offered to everyone; knowledge about the economy has to be increased by broader and deeper research and by pilot experiments on a wide front; and more people must be trained. Inter-African trade relations have to be de- veloped and greater cooperation encouraged by mieans of joint programs. This will build mutual interests and the habit of common efforts, creating a sure basis for increased regional integration, such as is envisaged in the Lagos Plan of Action. A strategy focused on agriculture and exports is thus open-ended, a necessary beginning. It will help generate the resources Africa needs to consolidate its political and administrativeforces,educateandimprovethehealth of its people, and find out what will work and ws will not. It will bring forth human hat talenit nowv neglected and uncover physical resources not yet imagined. In all societies, formnidable obstacles prevent quick responses to even the most carefully reasoned calls for change. In some cases, consumers and producers, parastatal managers, civil Nervants, ancd industrialists have an interest in maintaining existing policies, however inefficient these might be from a national point of view. For these reasons and others, Afncan governments will need additional outside assistance, and this matter is discussed in Chapter 9. The first step for the international community, if it is to assist African countries through the present crisis and help the region realize its potenitial, is a commitment to larger aid flow. While per capita aid to Africa is already relatively high, the needs are particularlY large and pressing when compared with those of most other developing re,ions w,hich are at roughly the same level of per capita 1ncome, Vhile it is emphasized the analysis in the Report suggests that a doubling of aid in real terms by the end of the 1980s, from $4. On the other hand, if the established patterns continue, the overall per capita growth rate will be zero or negative, with alarming possibilities for even steeper downward spirals in some countries. Additional aid commitments will have to be made now if disbursements are to reach required levels by the mid-1980s. These inflows should be targeted to improve efficiency of resource use in the short and medium term. Quick-disbursing balance-of-payments assistance is critically needed in some countries to permit fuller operation and maintenance of existing productive capacity and infrastructure. A focus on completion of existing projects, on making recently completed projects work better, on rehabilitation, and on maintenance will lead to quick increases in output.
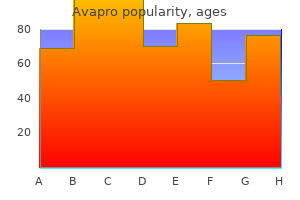
Increased oxalate levels can lead to the formation of kidney stones and diabetes medications list type 2 300 mg avapro, ultimately diabetes mellitus epocrates avapro 150mg with visa, to kidney failure. These observations highlight the need for a treatment that targets both conditions. Mononuclear cell infiltration was also massively increased, in particular in the perivascular areas. In the liver, inflammation and fibrosis were also attenuated, specifically in the periportal zone that has been shown to be correlated with the severity of the disease. Interestingly, the most significant responders in the liver were also the best responders in the kidneys. Amsterdam University Medical Centres, Amsterdam Universitair Medische Centra, Amsterdam, Netherlands. Background: Abnormal energy metabolism is considered to be related to renal interstitial fibrosis. N-lysine acetylation is an important post-translational modification involves in energy metabolism. Recently the innate immune system has been recognized as an important modulator of the inflammatory response during infection and tissue injury/repair. Primary culture of peritoneal macrophages isolated from these mice were used for in vitro study. Paul,6 James Dunbar,7 Andrea Taddei,7 Mark Davies,7 Siobhan McMahon,7 Andres Mori,7 Regina Fritsche-Danielson,8 Claus Bendtsen,4 Pernille B. Results: the fleet of models identified 295 potential targets that were triaged down to 69 targets. Subsequently, we will employ in vivo studies to confirm the mechanism of action for targets that had shown successful in vitro readouts. Eventually, we will progress targets with compelling novel biology within our renal portfolio. These clusters exhibited clear molecular phenotypes, permitting labeling as, proliferating, dedifferentiated-intermediate, dedifferentiated-regenerating, and (present only following injury) dedifferentiated-senescence. Each of these clusters exhibited a unique gene expression signature, including multiple genes associated with renal injury response and fibrosis progression. The transcription factor Twist1 limits pro-inflammatory cytokine production in T cells, but the role of T cell-derived cytokine mediators regulated by Twist1 in kidney damage has not been fully elucidated. Background: Sex differences in mitochondrial performance have been linked to many pathologies. Differences in the ability to manage oxidative stress, calcium uptake, fission/fusion cycles, and respiratory performance in mitochondria can affect the onset and progression of the diseases. While characteristic sex-related dissimilarities have been reported in renal function, nothing is known with regards to how sex may affect the performance of renal mitochondria. The goal of this study was to compare renal mitochondrial function in young healthy male vs female rats. In addition, we report that these parameters were lower in medullary vs cortical mitochondria, independent of sex. Conclusions: We report sex-related differences in mitochondrial function in the kidneys of young healthy rats. Further studies are needed to establish the mechanisms that they may affect the predisposition to kidney disease development later in life. Experiments to validate effect of butyrate on host epithelial cells in germ-free mice are underway. Conclusions: Resistant starch slows down the progression of chronic kidney disease in 5/6 nephrectomy model. All papers were screened, assessed and extracted by at least 2 researchers independently. To avoid duplicate of patient data, we matched the location, institution and time period, and only included the largest data source if studies overlapped. Prevalence of renal manifestations was pooled from studies that consecutively recruited patients from the general population, and with clear definition of outcome. Results: 36 studies from 8 countries and over 50 cities with a total of 14,712 patients were identified. We assumed capacity would be double this demand and that this demand would decrease to 25% during the pandemic.
References:
- https://medcraveonline.com/JNSK/JNSK-09-00382.pdf
- https://comenius.susqu.edu/biol/312/biochemistryofcheeseripening.pdf
- https://www.gamida-cell.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Gamida-Cell-Corporate-Presentation.pdf