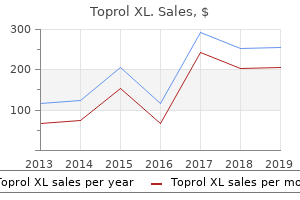
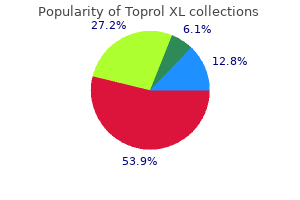
Toprol XL
"Discount toprol xl 50 mg otc, hypertension guideline update jnc 8."
By: Sarah Gamble PhD
- Lecturer, Interdisciplinary

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/sarah-gamble/
Selected patients may require plasma renin activity arrhythmia junctional buy 100mg toprol xl free shipping, 24 hour urine catecholamines arteria maxilar toprol xl 50 mg free shipping, or renal function testing (glomerular filtration rate and blood flow). Atenolol (Tenormin) initial dose 50 mg qd, then 50-100 mg qd, max 200 mg/d [25, 50, 100 mg]. Drug-induced Syncope: -Discontinue vasodilators, centrally acting hypotensive agents, tranquilizers, antidepressants, and alcohol use. Nursing: Pulse oximeter, bedside peak flow rate before and after bron chodilator treatments. Aminophylline and Theophylline (second-line therapy): -Aminophylline load dose: 5. Maintenance Treatment: -Salmeterol (Serevent) 2 puffs bid; not effective for acute asthma because of delayed onset of action. Aminophylline and Theophylline (second line therapy): -Aminophylline loading dose, 5. Admit to: Intensive care unit Diagnosis: Hemoptysis Condition: Vital signs: q1-6h. Anti-glomerular basement antibody, rheumatoid factor, complement, an ti-nuclear cytoplasmic antibody. Special Medications: Gastrointestinal Decontamination: -Gastric lavage if indicated for recent oral ingestion. Syringe: pH (2 mL collected anaerobically, heparinized on ice) Bag or Bottle: Cytology. Anticoagulant Overdose 37 Hematologic Disorders Anticoagulant Overdose Unfractionated Heparin Overdose: 1. Warfarin (Coumadin) Overdose: -Gastric lavage and activated charcoal if recent oral ingestion. Deep Venous Thrombosis Admit to: Diagnosis: Deep vein thrombosis Condition: Vital signs: q shift. Nursing: Guaiac stools, warm packs to leg prn; measure calf circumference qd; no intramuscular injections. Pulmonary Embolism Admit to: Diagnosis: Pulmonary embolism Condition: Vital signs: q1-4h. Sickle Cell Crisis 39 Sickle Cell Crisis Admit to: Diagnosis: Sickle Cell Crisis Condition: Vital signs: q shift. Nursing: Respiratory isolation, inputs and outputs, lumbar puncture tray at bedside. Infective Endocarditis Admit to: Diagnosis: Infective endocarditis Condition: Vital signs: q4h. Blood C&S x 3-4 over 24h, serum cidal titers, minimum inhibitory concentration, minimum bactericidal concentra tion. Nursing: Pulse oximeter, inputs and outputs, nasotracheal suctioning prn, incentive spirometry. Moderately ill Patients Without Underlying Lung Disease from the Community: -Cefuroxime (Zinacef) 0. Critically ill Patients: -Initial treatment should consist of a macrolide with 2 antipseudomonal agents for synergistic activity: -Erythromycin 0. Combination therapy with 3 agents (two nucleoside analogs and a protease inhibitor) is recommended as initial therapy. Didanosine (Videx, ddI) 200 mg bid for patients >60 kg; or 125 mg bid for patients <60 kg. Acute Toxoplasmosis: -Pyrimethamine 200 mg, then 50-75 mg qd, plus sulfadiazine 1. Septic Arthritis Admit to: Diagnosis: Septic arthritis Condition: Vital signs: q shift Activity: No weight bearing on infected joint. Passive range of motion exercises of the affected joint bid; otherwise, keep knee in resting splint. Initial treatment of life-threatening sepsis should include a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftizoxime or ceftriaxone), or piperacillin/tazobactam, or ticarcillin/clavulanic acid or imipenem, each with an aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin or amikacin). Intra-abdominal or pelvic infections, likely to involve anaerobes, should be treated with ampicillin, gentamicin and metronidazole; or either ticarcillin/clavulanic acid, ampicillin/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, imipenem, cefoxitin or cefotetan, each with an aminoglycoside. Febrile neutropenic patients with neutrophil counts <500/mm3 should be treated with vancomycin and ceftazidime, or piperacillin/tazobactam and tobramycin or imipenem and tobramycin. Blood Pressure Support -Dopamine 4-20 mcg/kg/min (400 mg in 250 cc D5W, 1600 mcg/mL).
In addition to fines blood pressure chart diastolic high buy toprol xl 100 mg online, offenders often face substantial costs for license reinstatement arrhythmia beta blocker toprol xl 25 mg overnight delivery, mandated alcohol education or treatment, insurance rate increases, and legal fees. The scanty information available suggests that fines at the levels currently imposed have little effect on reducing alcohol-impaired driving (Century Council, 2003, p. Eighteen States require some jail time for first offenders, though 11 of these States allow community service in lieu of jail. Forty-nine States require jail for third offenders, though even these offenders can substitute community service in 9 States. Jail is expensive: $16,500 per offender per year in Maryland and $27,500 in New Mexico, for example (Century Council, 2003; pp. Offenses with mandatory jail terms may be pled down, or judges simply may ignore the mandatory jail requirement (Robertson and Simpson, 2002b, pp. The effects of community service programs on alcohol-impaired driving have not been evaluated (Century Council, 2003, p. Use: A Century Council (1997) survey of the States reported that 16 States provide for diversion programs in State law or statewide practice, and local courts and judges in some additional States also offer diversion programs. In addition, if plea agreements are restricted, some charges may be dismissed or some offenders may request a full trial, resulting in significant costs. Restrictions and monitoring are relaxed as offenders demonstrate responsible behavior. Some individual program evaluations show that they are quite successful, with low recidivism rates. Follow-up costs may be greater because probation officer caseloads may need to be reduced to provide close monitoring and because judges must allocate time to meet regularly with probationers and to deal with any probation violations. Court monitoring provides data on how many cases are dismissed or pled down to lesser offenses, how many result in convictions, what sanctions are imposed, and how these results compare across different judges and different courts. Use: No data is available on the number of court monitoring programs currently active. It is generally believed that court monitoring has decreased substantially since the mid-1980s, when Probst et al. Time to implement: Court monitoring programs can be implemented very quickly if volunteer monitors are available. They likely will continue to drink and drive unless their alcohol problems are addressed. Alcohol problem assessment can take many forms, from a brief paper-and-pencil questionnaire to a detailed interview with a treatment professional. For brief overviews of alcohol assessment and treatment programs and further references see Century Council (2003, pp. Effectiveness: Even the best of the many assessment instruments currently in use is relatively inaccurate. Treatment appears to be most effective when combined with other sanctions and when offenders are monitored closely to assure that both treatment and sanction requirements are met (Century Council, 2003, p. Offenders can bear some of the costs of both assessment and treatment, though provisions must be made for indigent offenders. Both assessment and treatment require good record systems to track offenders and monitor progress. Other issues: · Treatment options: Alcohol assessment and treatment programs are long-term and expensive investments. States and communities should carefully weigh the costs and benefits of the many options available before implementing any. Close monitoring can be accomplished at various levels and in various ways, including a formal intensive supervision program, home confinement with electronic monitoring, dedicated detention facilities, and individual oversight by judges. New Mexico estimated that intensive supervision cost $2,500 per offender per year compared to $27,500 per offender per year for jail (Century Council, 2003, p. Dedicated detention facility costs can approach jail costs: $13,500 annually in Maryland for dedicated detention compared to $16,500 for jail (Century Council, 2003, p.
These are elective procedures which may not be appropriate in the district hospital arteria yahoo discount 50mg toprol xl with visa. The articular cartilage is primarily affected hypertension after pregnancy toprol xl 25mg on line, at first becoming rough and irregular and eventually being destroyed completely. Inflammatory or rheumatoid arthritis is secondary to an immune reaction that destroys the articular cartilage. Evaluation and diagnosis Degenerative arthritis Degenerative arthritis is characterized by: History Slow onset of pain with use Decreased motion and stiffness Mild swelling Examination Tenderness about the joint Palpable spurs at the joint margins Loss of motion 198 General orthopaedics X-ray Decreased cartilage space Sclerosis of bone about the weight bearing surfaces Spur formation Subchondral cysts. Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by: 19 History Joints painful and swollen with morning stiffness Multiple joints frequently affected Possible family history of similar problems Examination Joints swollen and tender with decreased range of motion Hands and feet frequently involved Deformity common 75 per cent of patients have dangerous laxity of the C1C2 vertebral bodies X-ray Decrease in cartilage space along with bone density Erosions at the joint margins are common Bone spurs are rare. During acute episodes of rheumatoid arthritis, splint the joint with a removable plaster dressing. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis may benefit from oral corticosteroid medication or other special drugs. Injections For degenerative arthritis, use intra-articular injections of cortisone with caution, as it often speeds up the cartilage deterioration. In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, cortisone helps to control the inflammation and periodic injections may be helpful. Muscle strengthening For both types of arthritis, try to preserve joint motion and extremity muscle strength. Surgery Surgery may be needed for end stage joint destruction or for lack of response to medical treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Corticosteroid injections into bursa are helpful, but they should not be used around large tendons. They are positioned between structures that move over each other and act to reduce friction. When subjected to increased pressure or excessive motion, they become inflamed, fill with fluid and are painful. Tendons are most vulnerable to inflammatory overuse symptoms in places where they attach to bone (the lateral epicondyle of the humerus) or travel within a surrounding sheath (the flexor tendons of the digits or the Achilles tendon at the ankle). Evaluation and diagnosis Make the diagnosis based on a history of overuse and the physical findings of tenderness, swelling and pain with use. Infectious bursitis is common at this location, so aspirate the bursa fluid and examine it for infection before treating as an inflammatory bursitis. Diagnose by history of pain with walking, pain while lying on the affected side and tenderness to palpation directly over and slightly posterior to the greater trochanter of the femur. It is caused by direct pressure on the anterior aspect of the knee from activities such as kneeling. The other bursa (pes anserine, infrapatella, fibular collateral) are irritated by excessive use associated with walking or climbing. As the tendons move in and out of the sheath, the nodule catches at the edge, causing the finger to "trigger" (snap into flexion or extension). The tendon is contained within a sheath and nodule formation or calcification of the tendon is common. Corticosteroid injections into bursa and tendon sheaths may help if other methods fail. Surgery Occasionally, surgical release of the tendon sheath is necessary to prevent continuing irritation of the tendon. If performed correctly, this first survey (the "primary survey") should identify such life-threatening injuries such as: Airway obstruction Chest injuries with breathing difficulties Severe external or internal haemorrhage Abdominal injuries. If there is more than one injured patient, treat patients in order of priority (triage). Its primary function is to diagnose and treat life threatening injuries which, if left undiagnosed and untreated, could lead to death: Airway obstruction Chest injuries with breathing difficulties Severe external or internal haemorrhage Abdominal injuries. When more than one life threatening state exists, simultaneous treatment of injuries is essential and requires effective teamwork. Chin lift/jaw thrust (tongue is attached to the jaw) Suction (if available) Guedel airway/nasopharyngeal airway Intubation; keep the neck immobilized in neutral position. If inadequate, consider: Artificial ventilation Decompression and drainage of tension pneumothorax/haemothorax Closure of open chest injury. Disability Make a rapid neurological assessment (is the patient awake, vocally responsive to pain or unconscious?

An analysis of community and hospital-acquired bacteraemia in a large teaching hospital in the United Kingdom blood pressure by palpation cheap toprol xl 50 mg fast delivery. The benefit of appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment in patients with bloodstream infection hypertension in 9th month of pregnancy order 100mg toprol xl overnight delivery. The influence of inadequate empirical antimicrobial treatment on patients with bloodstream infections in an intensive care unit. Inadequate antimicrobial treatment of infections: a risk factor for hospital mortality among critically ill patients. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: risk factors for mortality and influence of delayed receipt of effective antimicrobial therapy on clinical outcome. An international prospective study of pneumococcal bacteremia: correlation with in vitro resistance, antibiotics administered, and clinical outcome. Early administration of antibiotics does not shorten time to clinical stability in patients with moderate-to-severe community-acquired pneumonia. Reappraisal of community-acquired bacteremia: a proposal of a new classification for the spectrum of acquisition of bacteremia. Health care-associated bloodstream infections in adults: a reason to change the accepted definition of community-acquired infections. Clinical safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of murine monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. The effects of ibuprofen on the physiology and survival of patients with sepsis: the Ibuprofen in Sepsis Study Group. Epidemiology of bloodstream infection in nursing home residents: evaluation in a large cohort from multiple homes. Community-acquired bloodstream infection in critically ill adult patients: impact of shock and inappropriate antibiotic therapy on survival. Trends in antimicrobial resistance among urinary tract infection isolates of Escherichia coli from female outpatients in the United States. Antimicrobial resistance among uropathogens that cause community-acquired urinary tract infections in women: a nationwide analysis. Emergence and dissemination of quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli in the community. Frequency of pathogen occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility among communityacquired respiratory tract infections in the respiratory surveillance program study: microbiology from the medical office practice environment. Decreased susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones in Canada: Canadian Bacterial Surveillance Network. Effect of new susceptibility breakpoints on reporting of resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: United States, 2003. Increasing resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones: results of a Hong Kong multicentre study in 2000. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin or soft tissue infections in a state prison: Mississippi, 2000. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a meta-analysis of prevalence and risk factors. Outbreaks of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections-Los Angeles County, California, 20022003. Development of resistance during antimicrobial therapy: a review of antibiotic classes and patient characteristics in 173 studies. High prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in emergency department skin and soft tissue infections. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: is it in your community and should it change practice? Inducible clindamycin resistance in staphylococci: should clinicians and microbiologists be concerned? Streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome: spectrum of disease, pathogenesis, and new concepts in treatment. Improved outcome of clindamycin compared with beta-lactam antibiotic treatment for invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infection.
Discount toprol xl 50mg line. Tonya Brown | Part 27 | Blood Pressure Readings.
References:
- https://www.urology.uci.edu/pdf/UCIMensHealthFlyer2020F.pdf
- https://www.gilead.com/-/media/files/pdfs/remdesivir/eua-fact-sheet-for-hcps.pdf
- https://ameliaislandliving.com/fernandinabeach/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/amelia-island-bike-trail-map.pdf