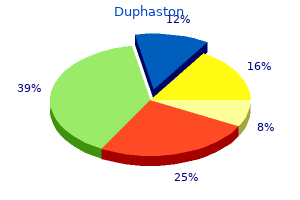
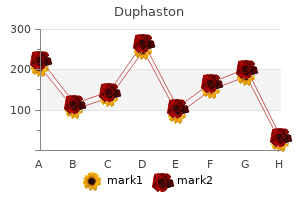
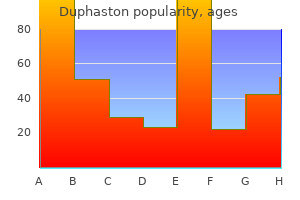
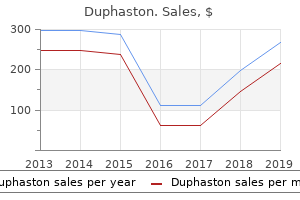
Duphaston
"Buy cheap duphaston 10 mg on-line, women's health issues class."
By: Amy Garlin MD
- Associate Clinical Professor

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/amy-garlin/
Transverse section of a primary villus showing a core of cytotrophoblastic cells covered by a layer of syncytium women's health weight loss pills purchase 10 mg duphaston free shipping. Transverse section of a secondary villus with a core of mesoderm covered by a single layer of cytotrophoblastic cells menstruation taboos buy 10 mg duphaston overnight delivery, which in turn is covered by syncytium. By the end of the third week, mesodermal cells in the core of the villus begin to differentiate into blood cells and small blood vessels, forming the villous capillary system. Capillaries in tertiary villi make contact with capillaries developing in the mesoderm of the chorionic plate and in the connecting stalk. These vessels, Tertiary stem villi in turn, establish contact with the intraembryonic circulatory system, connecting the placenta and the embryo. Hence, when the heart begins to beat in the fourth week of development, the villous system is ready to supply the embryo proper with essential nutrients and oxygen. Meanwhile, cytotrophoblastic cells in the villi penetrate progressively into the overlying syncytium until they reach the maternal endometrium. Syncytium Outer cytotrophoblast shell Intervillous spaces Connecting stalk Amniotic cavity Definitive yolk sac Chorionic plate Chorionic cavity Exocoelomic cyst Figure 5. Tertiary and secondary stem villi give the trophoblast a characteristic radial appearance. Intervillous spaces, which are found throughout the trophoblast, are lined with syncytium. Cytotrophoblastic cells surround the trophoblast entirely and are in direct contact with the endometrium. Chapter 5 Third Week of Development: Trilaminar Germ Disc 61 Maternal vessels Outer cytotrophoblast shell Syncytiotrophoblast Endometrium Intervillous space Cytotrophoblast Mesoderm core with capillaries Chorionic plate Connecting stalk Chorionic cavity Figure 5. Maternal vessels penetrate the cytotrophoblastic shell to enter intervillous spaces, which surround the villi. Capillaries in the villi are in contact with vessels in the chorionic plate and in the connecting stalk, which in turn are connected to intraembryonic vessels. Here they establish contact with similar extensions of neighboring villous stems, forming a thin outer cytotrophoblast shell. This shell gradually surrounds the trophoblast entirely and attaches the chorionic sac firmly to the maternal endometrial tissue. Villi that extend from the chorionic plate to the decidua basalis (decidual plate: the part of the endometrium where the placenta will form; see Chapter 8) are called stem or anchoring villi. Those that branch from the sides of stem villi are free (terminal) villi, through which exchange of nutrients and other factors will occur. The chorionic cavity, meanwhile, becomes larger, and by the 19th or the 20th day, the embryo is attached to its trophoblastic shell by a narrow connecting stalk. The connecting stalk later develops into the umbilical cord, which forms the connection between the placenta and embryo. Summary the most characteristic event occurring during the third week is gastrulation, which begins with the appearance of the primitive streak, which has at its cephalic end the primitive node. In the region of the node and streak, epiblast cells move inward (invaginate) to form new cell layers, endoderm and mesoderm. Cells that do not migrate through the streak but remain in the epiblast form ectoderm. Hence, epiblast gives rise to all three germ layers in the embryo, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, and these layers form all of the tissues and organs. Prenotochordal cells invaginating in the primitive pit move forward until they reach the prechordal plate. With further development, the plate detaches from the endoderm, and a solid cord, the notochord, is formed. It forms a midline axis, which will serve as the basis of the axial skeleton. Cephalic and caudal ends of the embryo are established before the primitive streak is formed. Formation of these structures in more caudal regions is regulated by the Brachyury (T) gene. Epiblast cells moving through the node and streak are predetermined by their position to become specific types of mesoderm and endoderm. Thus, it is possible to construct a fate map of the epiblast showing this pattern.
Gregg that rubella (German measles) affecting a mother 117 118 Part 1 General Embryology Risk of Birth Defects Being Induced Inc r eas i ng Risk First Prenatal Visit Parturition 0 3 5 Embryonic Period 8 Fetal Period 38 Weeks G e s t ation Figure 9 women's health clinic orlando cheap duphaston 10mg amex. During this time pregnancy zone protein cheap duphaston 10mg online, the risk for gross structural defects being induced decreases, but organ systems may still be affected. For example, the brain continues to differentiate during the fetal period, such that toxic exposures may cause learning disabilities or intellectual disability. The fact that most birth defects occur prior to the eighth week makes it imperative to initiate birth defects prevention strategies prior to conception. Unfortunately, most women do not appear for their first prenatal visit until the eighth week, which is after the critical time for prevention of most birth defects. Lenz linked limb defects to the sedative thalidomide and made it clear that drugs could also cross the placenta and produce birth defects. Since that time, many agents have been identified as teratogens (factors that cause birth defects) (Table 9. Strands of ammion may be swallowed or become wrapped around structures causing various disruption-type defects. Chapter 9 Birth Defects and Prenatal Diagnosis 119 metabolism, resistance to infection, and other biochemical and molecular processes that affect the conceptus. The most sensitive period for inducing birth defects is the third to eighth weeks of gestation, the period of embryogenesis. For example, cleft palate can be induced at the blastocyst stage (day 6), during gastrulation (day 14), at the early limb bud stage (fifth week), or when the palatal shelves are forming (seventh week). Furthermore, whereas most abnormalities are produced during embryogenesis, defects may also be induced before or after this period; no stage of development is completely safe. Mechanisms may involve inhibition of a specific biochemical or molecular process; pathogenesis may involve cell death, decreased cell proliferation, or other cellular phenomena. Principles of Teratology Factors determining the capacity of an agent to produce birth defects have been defined and set forth as the principles of teratology. They include the following: 1 Susceptibility to teratogenesis depends on the genotype of the conceptus and the manner in which this genetic composition interacts with the environment. The maternal genome is also important with respect to drug A were commonly produced by the drug thalidomide. Birth defects due to rubella (German measles) during pregnancy (congenital rubella syndrome) used to be a major problem, but development and widespread use of a vaccine have nearly eliminated congenital malformations from this cause. Often, the mother has no symptoms, but the effects on the fetus can be devastating. The infection can cause serious illness at birth and is sometimes Chapter 9 Birth Defects and Prenatal Diagnosis 121 fatal. On the other hand, some infants are asymptomatic at birth, but develop abnormalities later, including hearing loss, visual impairment, and intellectual disability. Herpes-induced abnormalities are rare and usually infection is transmitted to the child during delivery, causing severe illness and sometimes death. Intrauterine infection with varicella causes scarring of the skin, limb hypoplasia, and defects of the eyes and central nervous system. The occurrence of birth defects after prenatal infection with varicella is infrequent and depends on the timing of the infection. Other Viral Infections and Hyperthermia Malformations apparently do not occur following maternal infection with measles, mumps, hepatitis, poliomyelitis, echovirus, coxsackie virus, and influenza, but some of these infections may cause spontaneous abortion or fetal death or may be transmitted to the fetus. For example, coxsackie B virus may cause an increase in spontaneous abortion, while measles and mumps may cause an increase in early and late fetal death and neonatal measles and mumps. Hepatitis B has a high rate of transmission to the fetus, causing fetal and neonatal hepatitis; whereas hepatitis A, C, and E are rarely transmitted transplacentally. Also, there is no evidence that immunizations against any of these diseases harm the fetus. A complicating factor introduced by these and other infectious agents is that most are pyrogenic (cause fevers), and elevated body temperature (hyperthermia) caused by fevers or possibly by external sources, such as hot tubs and saunas, is teratogenic. Characteristically, neurulation is affected by elevated temperatures and neural tube defects, such as anencephaly and spina bifida, are produced. Poorly cooked meat; feces of domestic animals, especially cats; and soil contaminated with feces can carry the protozoan parasite Toxoplasmosis gondii. A characteristic feature of fetal toxoplasmosis infection is cerebral calcifications.
Evaluation of respiratory protection programs and practices in California hospitals during the 2009-2010 H1N1 164 influenza pandemic breast cancer zip hoodies buy duphaston 10mg visa. Correlation of respirator fit measured on human subjects and a static advanced headform pregnancy 9 weeks symptoms trusted 10mg duphaston. Influenza vaccination coverage among health care personnel - United States, 2015-16 influenza season. Evaluation of Minnesota and Illinois hospital respiratory protection programs and health care worker respirator use. Potential Exposure to Ebola Virus from Body Fluids due to Ambulance Compartment Permeability in Sierra Leone. Interim recommendations for facemask and respirator use to reduce 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus transmission. Interim guidance on infection control measures for 2009 H1N1 influenza in healthcare settings, including protection of healthcare personnel. Questions and answers about updating guidance on infection control measures for influenza in healthcare settings. Questions and answers regarding respiratory protection for preventing 2009 H1N1 influenza among healthcare personnel. Potential work-related bloodborne pathogen exposures by industry and occupation in the United States Part I: An emergency department-based surveillance study. Baseline evaluation with a sweating thermal manikin of personal protective ensembles recommended for use in West Africa. Community Hospital to Care for Patients With Ebola Virus Disease: Context for National Recommendations and Future Strategies Ebola Infection Prevention and Control in a Community Hospital. Sensitivity analysis of important parameters affecting contact pressure between a respirator and a headform. Evaluation of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus exposure among internal medicine housestaff and fellows, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, Utah. The Effectiveness of Using Interferon-gamma Release Assays in Screening Immigration Employees for Latent Tuberculosis Infection. Evaluation of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) exposures and illness among physicians in training. Natural infection of guinea pigs exposed to patients with highly drug-resistant tuberculosis. Rapid impact of effective treatment on transmission of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Effectiveness of a Local Ventilation/Filtration Intervention for HealthCare Worker Exposure Reduction to Airborne Infection in a Hospital Room. Authorization of emergency use of certain personal respiratory protection devices: availability. Premarket notification requirements concerning gowns intended for use in health care settings. The effect of soil accumulation on multiple decontamination processing of N95 filtering facepiece respirator coupons using physical methods. Considerations for recommending extended use and limited reuse of filtering facepiece respirators in health care settings. Validation and application of models to predict facemask influenza contamination in healthcare settings. Fatigue increases the risk of injury from sharp devices in medical trainees results from a case-crossover study. Non-hospital based registered nurses and the risk of bloodborne pathogen exposure. Prevalence and risk factors for bloodborne exposure and infection in correctional healthcare workers. The prevalence and risk factors for percutaneous injuries in registered nurses in the home health care sector. Challenge of N95 filtering facepiece respirators with viable H1N1 influenza aerosols. Development of an empirical model to aid in designing airborne infection isolation rooms.
Others need to combine with other proteins or be released from sequestered sites or be targeted to specific cell regions women's health clinic jackson hole buy 10mg duphaston overnight delivery. Thus pregnancy recipes buy cheap duphaston 10 mg, there are many regulatory levels for synthesizing and activating proteins, such that although only 23,000 genes exist, the potential number of proteins that can be synthesized is probably closer to five times the number of genes. In fact, this splicing process provides a means for cells to produce different proteins from a single gene. For example, by removing different introns, exons are "spliced" in different patterns, a process called alternative splicing. Proteins derived from the same gene are called splicing isoforms (also called splice variants or alternative splice forms), and these afford the opportunity for different cells to use the same gene to make proteins specific for that cell type. Even after a protein is made (translated), there may be post-translational modifications that affect its function. Most often, one group of cells or tissues causes another set of cells or tissues to change their fate, a process called induction. In each such interaction, one cell type or tissue is the inducer that produces a signal, and one is the responder to that signal. The capacity to respond to such a signal is called competence, and competence requires activation of the responding tissue by a competence factor. Epithelial cells are joined together in tubes or sheets, whereas mesenchymal cells are fibroblastic in appearance and dispersed in extracellular matrices. Based on these sites, different introns are "spliced out" to create more than one protein from a single gene. Following an initial signal from one tissue, a second tissue is induced to differentiate into a specific structure. Once the induction process is initiated, signals (arrows) are transmitted in both directions to complete the differentiation process. Although an initial signal by the inducer to the responder initiates the inductive event, crosstalk between the two tissues or cell types is essential for differentiation to continue. These lines of communication are established by paracrine interactions, whereby proteins synthesized by one cell diffuse over short distances Paracrine Signaling Paracrine factors act by signal transduction pathways either by activating a pathway directly or by blocking the activity of an inhibitor of a pathway (inhibiting an inhibitor, as is the case with hedgehog signaling). Signal transduction pathways include a signaling molecule (the ligand) and a receptor. The receptor spans the cell membrane and has an extracellular domain (the ligand-binding region), a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. When a ligand binds its receptor, it induces a conformational change in the receptor that activates its cytoplasmic domain. In turn, phosphorylation activates these proteins to phosphorylate additional proteins, and thus a cascade of protein interactions is established that ultimately activates a transcription factor. The pathways are numerous and Ligand Receptor complex Cell membrane P P P P Activated (kinase) region Nuclear pores P Cytoplasm P Activated protein Activated protein complex Activated protein complex acts as a transcription factor P Nucleus Figure 1. Typically, the activation is enzymatic involving a tyrosine kinase, although other enzymes may be employed. Ultimately, kinase activity results in a phosphorylation cascade of several proteins that activates a transcription factor for regulating gene expression. Chapter 1 Introduction to Molecular Regulation and Signaling 7 complex and in some cases are characterized by one protein inhibiting another that in turn activates another protein (much like the situation with hedgehog signaling). Juxtacrine Signaling Juxtacrine signaling is mediated through signal transduction pathways as well but does not involve diffusable factors. Instead, there are three ways juxtacrine signaling occurs: (1) A protein on one cell surface interacts with a receptor on an adjacent cell in a process analogous to paracrine signaling. The Notch receptor protein extends across the cell membrane and binds to cells that have Delta, Serrate, or Jagged proteins in their cell membranes. Binding of one of these proteins to Notch causes a conformational change in the Notch protein such that part of it on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane is cleaved. The cleaved portion then binds to a transcription factor to activate gene expression.
Purchase 10 mg duphaston otc. Womens health issues.
References:
- https://jag.journalagent.com/sislietfaltip/pdfs/SETB_30_1_99_101.pdf
- http://whoville.ucsd.edu/PDFs/383_Squire_etal_%20AnnRevNeurosci2004.pdf
- https://www.unmc.edu/intmed/divisions/id/asp/news/docs/antimicrobial-renal-dosing-guidelines.pdf
- https://dukespace.lib.duke.edu/dspace/bitstream/handle/10161/16070/JCI96702.pdf