Medrol
"16 mg medrol with amex, arthritis questionnaire."
By: Brent Fulton PhD, MBA
- Associate Adjunct Professor, Health Economics and Policy

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/brent-fulton/
Prolactin and leptin levels were significantly less in the high dose group arthritis relief for horses medrol 4 mg online, and dopamine signaling to the pituitary was greater than controls at 26 weeks arthritis in the feet and hands generic medrol 4mg with visa. Based on the data, a mode of action (MoA) is established that begins with decreased food utilization, fat pad weight and body weight, reflected by the decreased leptin levels. As a consequence, there is altered hypothalamic signaling that results in altered pattern of transition into reproductive senescence. The longer time spent in persistent estrus and greater exposure to circulating estrogens leads to the observed increase in uterine adenocarcinomas. Fundamental differences exist between rats and humans in the control of reproductive senescence. Onset of senescence in rats is due to altered signaling within the hypothalamus, while menopause and reproductive senescence in humans is driven by depletion of a set number of primordial follicles in the ovaries with aging. The physiological difference in control of the reproductive cycle and the transition into reproductive senescence between rats and humans indicate that the established MoA leading to uterine tumor formation in rats is not relevant to humans. Kaushik, American Association for Cancer Research Brain tumor is considered as one of the most aggressive and incurable form of cancer. Even though advanced treatments such as surgical removal, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are available, brain tumor persists to be lethal. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation, characterized by pro-inflammatory adipokine production and macrophage activation/polarization is associated with increased risk of breast cancer. Adipocyte fatty acid composition is influenced by dietary intake and may regulate pro-inflammatory adipokine secretion. The adipokine profile from the fish oil-fed rats was shifted towards adipokines associated with reduced inflammation compared to the rats fed the western diet. The M1/M2 macrophage ratio decreased by 50% in adipose of fish oil fed rats compared to that from rats fed the western diet. Modulating the adipokine secretome with dietary interventions therefore may alter stromal-epithelial signaling that plays a role in controlling mammary stem cell self-renewal. The goal of this study is to understand whether breast epithelial cells have the same physiological and transcriptional response to endogenous progesterone and synthetic progestins. First, a dose course was conducted to determine the effects on cell proliferation, as growth arrest is a hallmark of progesterone exposure. Next, gene expression changes were assayed at physiologically relevant doses for both P4 (200nM) and the progestins (2nM). These results demonstrate that progestin compounds are able to elicit similar proliferative and gene expression responses as P4 at much lower concentrations. Future work will focus on transcriptome level differences between P4 and progestins. A novel alternative theory explains the combined study data: Cancer arises most efficiently in any tissue from not just any stem cell with critical mutations, but only from a stem cell that has or will become activated to an epigenetically mediated and maintained state of adaptive/regenerative hyperplasia-a state normally triggered by immune cells that generate and coordinate local inflammation at the site of tissue injury. Importantly, because inflammation typically has a substantially sublinear low-dose dose-response, the new theory predicts that a similar low-dose dose-response pattern pertains to most (perhaps all) environmental carcinogens. Sphingolipids are known to affect cancer progression by regulating cell death (apoptosis) and survival (autophagy). Whereas apoptosis is promoted by elevations in sphingosine and ceramide, increases in sphingosine-1-phosphate and ceramide-1-phosphate can tip the balance toward survival. Mechanistic evidence can aid in identifying carcinogens when human data are less than sufficient. Here we review important recent evaluations that were influenced by strong mechanistic evidence, and highlight types of evidence most influential in classifications of cancer hazard. In 1997, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin was first classified in Group 1 (carcinogenic to humans) based on sufficient evidence in animals and mechanistic considerations, an evaluation later confirmed by sufficient evidence in exposed humans in 2012. More recently, tetrachloroazobenzene was classified as "probably carcinogenic to humans" (Group 2A) because it belongs, on the basis of mechanistic considerations, to this same class of agents. Furthermore, in 2016, an upgrade from Group 2B to Group 2A was warranted for tetrabromobisphenol A, because it modulates receptor-mediated effects in combination with other key characteristics of carcinogens. Evidence that an agent is genotoxic has also been the basis for several mechanistic upgrades (ethylene oxide was the first one in 1994). More recently, in 2014, based on sufficient evidence in animals and strong mechanistic evidence that 1,3-propane sultone is genotoxic, the overall classification for this agent was upgraded from Group 2B to Group 2A. Mechanistic information, including evidence that an agent is genotoxic and modulates receptor-mediated effects, can thus provide early, robust evidence for carcinogenicity. Mechanisms can also be the basis for downgrades of the overall evaluation, when the mechanistic data satisfy the relevant criteria.
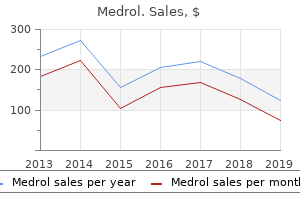
Infectious complications in lupus nephritis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis arthritis in hands and feet diet cheap medrol 16 mg line. Primary prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with connective tissue diseases degenerative arthritis in my back cheap medrol 4 mg without a prescription. Safety and efficacy of upfront graded administration of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in systemic lupus erythematosus: A retrospective cohort study. High prevalence of asymptomatic vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women receiving chronic glucocorticoid therapy: a cross-sectional outpatient study. Population-based assessment of adverse events associated with long-term glucocorticoid use. A systematic review and meta-analysis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in children. Protecting Bone Health in Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases: Pharmacological Considerations. Association of glomerular podocytopathy and nephrotic proteinuria in mesangial lupus nephritis. Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis with podocytopathy: a special entity of lupus nephritis. Glucocorticoid with or without additional immunosuppressant therapy for patients with lupus podocytopathy: a retrospective single-center study. Combination therapy with pulse cyclophosphamide plus pulse methylprednisolone improves long-term renal outcome without adding toxicity in patients with lupus nephritis. Mycophenolate mofetil or tacrolimus compared with intravenous cyclophosphamide in the induction treatment for active lupus nephritis. Comparison of low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide with oral mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of lupus nephritis. The 10-year follow-up data of the Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial comparing low-dose and high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Efficacy and safety of multitarget therapy with cyclophosphamide and tacrolimus for lupus nephritis: a prospective, single-arm, single-centre, open label pilot study in Japan. Long-term outcome of patients with diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis treated with prednisolone and oral cyclophosphamide followed by azathioprine. Predictors of long-term renal outcome in lupus nephritis trials: lessons learned from the Euro-Lupus Nephritis cohort. Long-term data on corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil treatment in lupus nephritis. A controlled trial of pulse cyclophosphamide versus pulse methylprednisolone in severe lupus nephritis. Comparing the efficacy of low-dose vs high-dose cyclophosphamide regimen as induction therapy in the treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis: a single center study. Comparison of high and low dose of cyclophosphamide in lupus nephritis patients: a long-term randomized controlled trial. A comparative study of two intensified pulse cyclophosphamide remission-inducing regimens for diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: an Egyptian experience. Is mycophenolate mofetil superior to pulse intravenous cyclophosphamide for induction therapy of proliferative lupus nephritis in Egyptian patients? Mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide in indian patients with lupus nephritis: Which is better? Low dose mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide in the induction therapy of lupus nephritis in Nepalese population: a randomized control trial. A cost-utility analysis of alternative drug regimens for newly diagnosed severe lupus nephritis patients in Thailand. Cost comparison between mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide-azathioprine in the treatment of lupus nephritis. The cost-effectiveness of mycophenolate mofetil as firstline therapy in active lupus nephritis. The humanistic and economic burden of systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Comparison of Lupus Nephritis Induction Treatments in a Hispanic Population: A Single-center Cohort Analysis.
Habitat Adult: In small intestine of man Larvae: In muscular tissues of cattle Eggs: In faeces of man or in gravid segments arthritis pain on shoulder medrol 16 mg amex. Colour: ivory white Scolex (head): quadrate rheumatoid arthritis depression buy medrol 16mg amex, with four suckers, no looks, no rostellum Strobila: 1000-2000 proglottides Parasitology 118 Mature Proglottides: Broader than long Genital pores are arranged irregularly alternate on the lateral margin of each segment Gravid proglottide Detach when fully develop and pass through the anus independently. Larvae: Known as Cysticercus bovis Found in skeletal and muscular tissues of cattle Has four suckers and no rostellum and hooklets Egg (Embryophore): identical with the egg of T. Size: - 33-40 m Shape: -Round Colour: - Shell-dark yellowish-brown, content light yellowish gray. Shell:-Thick, Smooth, brown, radially straited (embryophore) Content: - A round granular mass enclosed by a fine membrane with six hooklets Stains red (acid fast) in Ziehl-Neelsen staining technique, this character helps to differentiate from T. Egg(hexacanth embryolarva(Cysticercus bovis) Adult Parasitology 119 Man acquires infection from raw or under cooked infected meat. Following ingestion, the larvae become attached to the wall of the small intestine with its suckers. Proglottides are formed from the neck region and the larvae grow into a long adult tapeworm. When fully developed the gravid segments become detached and the eggs are discharged only after the gravid segments have been separated from the worm. Gravid segments containing eggs and eggs from ruptured segments are passed in the faeces. The embryos escape from the eggs and pass through the intestinal wall into a blood vessel. Through the blood circulation they are carried to muscles and develop into infective cystic larvae called cysticercus bovis. TheScientific Book Center, Cairo) Parasitology 120 Pathogenicity: - Causes taeniasis Major symptoms are loss of appetite, weight loss, hunger, acute intestinal obstruction, eosinophilia, and discomfort by the crawling of segments through the anus. Avoid eating raw or insufficiently cooked meat which may contain infective larvae. Identifying gravid segments and scolex recovered from clothing or passed in faeces. Owing to the inherent problem of missing many infections during routine stool examination. Estimates made by different investigators of the prevalence Parasitology 121 of taeniasis in Ethiopia vary widely, from 2% -16% to over 70% (Kloos H et al, 1993, Yared M et al 2001). Taeniasis is so common in the country and the tradition of self-treatment is so well developed that most people do not use the health services for diagnosis and treatment. Instead, Ethiopians use about dozens of traditional plant medicines, including Kosso (Hagenia abyssinica). Enkoko (Embelia schimperi), and Metere (Glinus lotoides) upon noticing proglottids in the feces or when experimenting abdominal discomfort, usually every 2 months (Shibru T, 1986). Taenia solium (Pork tape worm) Geographical Distribution:-Widely distributed where human faeces reach pigs and pork is eaten raw or insufficiently cooked. Habitat: Adult: In the small intestine of man Larva: In muscular tissues of pig Egg: In the faeces of man and in gravid segment. Larvae:Known as Cysticercus cellulosae Found in skeletal and muscular tissues of pig Has four sucers, rostellum and two raws of hooklets Egg (embryophore): -morphologically identical with the egg of T. Size: - 31-43 (m Shape: -Round Colour:- Shell-dark yellowish-brown, content light yellowish gray. Shell: -Thick, Smooth, brown, radially straighten (embryophore) Content: - A round granular mass enclosed by a fine membrane with 6 hooklets. Does not stains red (acid fast) in Ziehl-Neelsen staining technique Life Cycle: the life cycle of T. Egg(hexacanth embryo) larva(Cysticercus cellulosae) Adult Parasitology 123 Man acquires infection from eating raw or under cooked pork that develops into adult in the intestine or from contaminated food or drink with faeces containing the eggs and develops into larval stage in visceral organs. Mode of Transmission can be Eating raw or under cooked pork meat Eggs in food or drink Internal autoinfections Pathology: Taeniasis and cysticercosis Major symptoms are as a result of the adult worm.
Order medrol 4mg with visa. Rheumatoid Arthritis (2016 May) - by Neelakshi Patel MD.
Insecticides are often not locally available or are too expensive for smallholder farmers arthritis webmd generic medrol 4 mg fast delivery. Health problems related to misuse of insecticides (Coulibaly and Lowenberg-DeBoer arthritis in my dog's hips order 4mg medrol, 2002; Maumbe and Swinton, 2003) are another reason for considering alternative solutions to the podborer problem. Hairy caterpillar In the Sahelian zone, which is the second most important area where cowpeas are grown, insect pest pressure is low but on occasions hairy caterpillar (Amsacta moorie Butler syn. Amsacta moloneyi Druce) can totally destroy large areas of the crop and cultivar resistance is not available. At the beginning of the rainy season in the Sahelian zone of Senegal, waves of female Amsacta moths emerge and lay eggs on a large range of plant species (Ndoye, 1978). They will feed on a range of grasses, pearl millet, sorghum and peanut but they show preference for cowpea. If the cowpea plants are young when they are infested, they are defoliated and killed. If the cowpea plants are large, they can outgrow the attack and are only partially defoliated. Usually, however, the waves of hairy caterpillars arrive when the cowpea plants are young. Hairy caterpillar can be controlled by synthetic insecticides; however, farmers usually do not have the spraying equipment or supplies of insecticide to enable them to control the sporadic large waves of hairy caterpillar that occasionally occur in the Sahelian zone. Pest predators As in all cropping systems there are a variety of natural enemies feeding/developing on cowpea insect pests. These natural enemies include more than 25 parasitoid species belonging to the families listed in Table 5. These include mites, beetles, ants, bugs and spiders (Bottenberg, Tamт and Singh, 1998; Adati et al. Parasitoids and entomoviruses attacking the podborer Maruca vitrata in West Africa Parasitoids Hymenoptera, Trichogrammatidae Trichogrammatoidea eldanae Hymenoptera, Eulophidae Tretrastichus sp. Biotechnological developments Biotechnological approaches in cowpea improvement the goal of cowpea breeding programmes is to develop consumer-preferred varieties with high yield and resistance to biotic and abiotic constraints to production. Traditional plant-breeding approaches to cowpea improvement have had many successes over the last 30 years. Three principal methods are used in breeding the self-pollinating cowpea: pedigree, mass selection and single seed descent. The pedigree method, often with slight modifications, is the one most frequently used. Selections are based largely on the main character of interest, for example, resistance to the parasitic weed Striga. Detailed data on maturity, time to flower, growth habit, and grain and fodder yields are collected and the most promising single plants selected for advancement. Other traits of interest are selected for as well, including seed colour, seed texture, seed size and leaf yield. The relative importance of these traits varies with the particular breeding programme. For example, leaf yield is more important in eastern and southern Africa while west and central African breeding projects lay more emphasis on grain and fodder yields. Over the years, improvements have resulted in more than a doubling of the average yield of the crop, from about 200 kg/ha to about 500 kg/ha. However, even this still-modest level of productivity can only be guaranteed if one or two insecticide sprays are applied. Unfortunately, there are no utilisable resistance genes for post-flowering insect pests in the cowpea genome. Cowpea is extremely well-isolated from other Vigna species that might provide sources of resistance genes. Many efforts have sought to create viable wide crosses between cowpea and its nearest relatives, but the gulf has proven too wide.
References:
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/0901/afp20140901p303.pdf
- https://www.bidmc.org/-/media/files/beth-israel-org/centers-and-departments/rehabilitation-services/otpt-pelvic-floor-abdominal-massage.pdf
- https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/cancer-horizon-scan-high-impact-1506.pdf