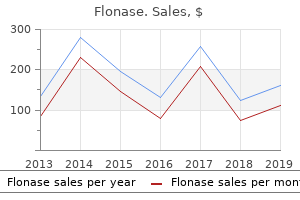
Flonase
"Buy discount flonase 50mcg on-line, allergy medicine cream."
By: Amy Garlin MD
- Associate Clinical Professor

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/amy-garlin/
Even among patients pursuing life-sustaining therapy allergy symptoms for amoxicillin buy discount flonase 50mcg on-line, initiating palliative care simultaneously with ongoing disease-focused therapy may be beneficial allergy shots dosage schedule cheap flonase 50mcg with visa. Released January 28, 2014 How this List Was Created this document was prepared as an initiative of the Critical Care Societies Collaborative, which includes the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses, the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Thoracic Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Each of these four societies was invited to nominate up to three members to join the taskforce. The final taskforce included 10 members representing all four societies and the disciplines of internal medicine, surgery, anesthesiology, emergency medicine and critical care nursing. The taskforce evaluated each item on five criteria (evidence, prevalence, cost, relevance, innovation), and agreed to narrow the list to 16 items. The taskforce debated the conceptual merits of these 16, and selected nine in which to pursue in-depth evidence reviews and consultations with external content experts. Taskforce members then independently scored each item on a scale from 1-9, rating each item on its overall impact as well as on each of the five criteria. The five items with the best mean overall scores were retained in the "penultimate" list. The executive committees sought feedback from additional experts in the field, debated the items and provided written comments to the taskforce. The disclosure and conflict of interest policies for the American Association of Critical Care Nurses, the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Thoracic Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine can be found at www. Routine chest x-rays in intensive care units: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Association of blood transfusion with increased mortality in myocardial infarction. Optimisation of energy provision with supplemental parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Executive Summary. Effect of a nursing-implemented sedation protocol on the duration of mechanical ventilation. Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled trial): a randomized controlled trial. Clinical practice guidelines for the sustained use of sedatives and analgesics in the critically ill adult. Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. Daily sedation interruption in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients cared for with a sedation protocol: a randomized controlled trial. Use of intensive care at the end of life in the United States: an epidemiologic study. Missed opportunities during family conferences about end-of-life care in the intensive care unit. To learn more about the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses, the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Thoracic Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine, please visit www. Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question 1 Avoid routine multiple daily self-glucose monitoring in adults with stable type 2 diabetes on agents that do not cause hypoglycemia. Once target control is achieved and the results of self-monitoring become quite predictable, there is little gained in most individuals from repeatedly confirming. There are many exceptions, such as for acute illness, when new medications are added, when weight fluctuates significantly, when A1c targets drift off course and in individuals who need monitoring to maintain targets. Self-monitoring is beneficial as long as one is learning and adjusting therapy based on the result of the monitoring. Because 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is the active form of vitamin D, many practitioners think that measuring 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is an accurate means to estimate vitamin D stores and test for vitamin D deficiency, which is incorrect. Current Endocrine Society guidelines recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in individuals at risk for deficiency.
There is a low risk of metastases and also a risk of detecting findings unrelated to the melanoma allergy testing jobs purchase flonase 50 mcg visa. Imaging should be performed if there are concerning findings on history and physical exam how many allergy shots until maintenance flonase 50 mcg cheap, and such tests should be driven by symptoms. As a means of refining the list of Choosing Wisely measures, the Quality Committee elected to include the five measures impacting the largest number of patients. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in elderly patients with breast cancer and no palpable axillary nodes: results after 15 years of follow-up. Recommendations for breast cancer surveillance for female survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancer given chest radiation: a report from the International Late Effects of Childhood Cancer Guideline Harmonization Group. Follow-up care, surveillance protocol, and secondary prevention measures for survivors of colorectal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline endorsement. Cipe G, Ergul N, Hasbahceci M, Firat D, Bozkurt S, Memmi N, Karatepe O, Muslumanoglu M. Evaluation of staging chest radiographs and serum lactate dehydrogenase for localized melanoma. The mission of the Society of Surgical Oncology is to improve multidisciplinary patient care by advancing the science, education and practice of cancer surgery worldwide. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question Patients who have no cardiac history and good functional status do not require preoperative stress testing prior to non-cardiac thoracic surgery. In highly functional asymptomatic patients, management is rarely changed by preoperative stress testing. Unnecessary stress testing can be harmful because it increases the cost of care and delays treatment without altering surgical or perioperative management in a meaningful way. Furthermore, low-risk patients who undergo preoperative stress testing are more likely to obtain additional invasive testing with risks of complications. Cardiac complications are significant contributors to morbidity and mortality after non-cardiac thoracic surgery, and it is important to identify patients preoperatively who are at risk for these complications. Cardiac stress testing can be an important adjunct in this evaluation, but it should only be used when clinically indicated. In addition, a recent consensus report from the United Kingdom questioned whether neurologic sequellae developing in cardiac surgery patients with asymptomatic carotid disease are due to the carotid artery disease or rather act as a surrogate for an increased stroke risk from atherosclerotic issues with the aorta. The Northern Manhattan Stroke Study concluded that carotid auscultation had poor sensitivity and positive predictive value for carotid stenosis and so decisions on obtaining carotid duplex studies should be considered based on symptoms or risk factors rather than findings on auscultation. It provides information regarding the integrity of the repair and allows the opportunity for early identification of problems that may need to be addressed surgically during the index hospitalization. Unlike valve repair, there is a lack of evidence that supports the routine use of cardiac echocardiography pre-discharge after cardiac valve replacement. This practice of routine screening for occult brain metastases has not been evaluated by a randomized clinical trial and may not be cost-effective or medically necessary. Risk models for cardiac surgery developed from review of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery Database incorporate a variable for chronic lung disease. In the absence of respiratory symptoms or suggestive medical history, pulmonary function testing is quite unlikely to change patient management or assist in risk assessment. Although some data are beginning to emerge about preoperative pulmonary rehabilitation prior to cardiac surgery for patients with even mild to moderate obstructive disease, this does not directly extrapolate to asymptomatic patients. The initial 17 recommendations from these Workforces were narrowed down to eight based upon frequency, clinical guidelines and potential impact. Guidelines for preoperative cardiac risk assessment and perioperative cardiac management in non-cardiac surgery. The task force for preoperative cardiac risk assessment and perioperative cardiac management in non-cardiac surgery of the European Society of Cardiology and endorsed by the European Society of Anaesthesiology. Non-invasive cardiac stress testing before elective major non-cardiac surgery: Population based cohort study. Temporal onset, risk factors, and outcomes associated with stroke after coronary artery bypass grafting. Stroke after cardiac surgery and its association with asymptomatic carotid disease: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
She reports having had no fever allergy testing mackay qld buy flonase 50 mcg without a prescription, weight loss allergy medicine yorkie order 50mcg flonase amex, leg weakness, or urinary or bowel dysfunction. Physical examination reveals weakness of her left triceps, finger extensors, and wrist flexors, as well as hypoesthesia of the third digit and a diminished triceps reflex. Cervical radiculopathy is a neurologic condition characterized by dysfunction of a cervical spinal nerve, the roots of the nerve, or both. It usually presents with pain in the neck and one arm, with a combination of sensory loss, loss of motor function, or reflex changes in the affected nerve-root distribution. At the last follow-up, 90 percent of the patients had normal findings or were only mildly incapacitated owing to cervical radiculopathy. In contrast to disorders of the lumbar spine, herniation of the nucleus pulposus is responsible for only 20 to 25 percent of cases. Foraminal encroachment of the spinal nerve from degenerative changes in the uncovertebral and zygapophyseal joints and herniation of the nucleus pulposus are the two most common causes of cervical radiculopathy (Panel A). Although the sensory symptoms (including burning, tingling, or both) typically follow a dermatomal distribution, the pain is more commonly referred in a myotomal pattern. Holding the affected arm on top of the head22 or moving the head to look down and strategies and evidence away from the symptomatic side often improves clinical diagnosis the pain, whereas rotation of the head or bending it There are no universally accepted criteria for the toward the symptomatic side increases the pain. The new england journal of medicine low back pain may be applied to the patient with neck pain and radiculopathy. Findings on physical examination vary depending on the level of radiculopathy and on whether there is myelopathy (Tables 1 and 2). In most series, the nerve root that is most frequently affected is the C7, followed by the C6. Reasonable indications include the presence of symptoms or signs of myelopathy, red flags suggestive of tumor or infection, or the presence of progressive neurologic deficits. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be useful in distinguishing the extent of bony and C-reactive protein levels are elevated in many spurs, foraminal encroachment, or the presence of Table 1. Typically, abnormal insertional activity, including positive sharp-wave potentials and fibrillation potentials, is present in the limb muscles of the involved myotome within three weeks of the onset of nerve compression. In addition, the presence of abnormal findings in paraspinal muscles differentiates cervical radiculopathy from brachial plexopathy. On the basis of anecdotal experience, analgesic agents, including opioids and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, are often used as first-line therapy. In patients with acute pain, some physicians advocate a short course of prednisone (for example, starting at a dose of 70 mg per day and decreasing by 10 mg every day). Retrospective40,41 and prospective42,43 cohort studies have reported favorable results with translaminar and transforaminal epidural injections of corticosteroids, with up to 60 percent of patients reporting long-term relief of radicular and neck pain and a return to usual activities. However, complications from these injections, although rare, can be serious and include severe neurologic sequelae from spinal cord or brainstem infarction. Some investigators have advocated the use of short-term immobilization (less than two weeks) with either a hard or a soft collar (either continuously or only at night) to aid in pain control. Cervical traction consists of administering a distracting force to the neck in order to separate the cervical segments and relieve compression of nerve roots by intervertebral disks. Common In appropriate patients, surgery may effectively re- surgical procedures for cervical radiculopathy are lieve otherwise intractable symptoms and signs re- shown in Figure 2. For such patients, are also signs of spinal cord impairment, since the anterior approaches (preferred in patients with a latter can lead to progressive and potentially irre- cervical kyphosis) include cervical diskectomy and versible neurologic deficits over time. Posterior options, which are often used in cases of multilevel decompressions in which there is preserved cervical lordosis, include laminectomy (with or without instrumented fusion) and laminoplasty (involving decompression and reconstruction of the laminae). Data from prospective observational studies indicate that two years after surgery for cervical radiculopathy without myelopathy, 75 percent of patients have substantial relief from radicular symptoms (pain, numbness, and weakness). In one randomized trial comparing surgical and nonsurgical therapies among 81 patients with radiculopathy alone, the patients in the surgical group had a significantly greater reduction in pain at three months than the patients who were assigned to receive physiotherapy or who underwent immobilization in a hard collar (reductions in visual-analogue scores for pain: 42 percent, 18 percent, and 2 percent, respectively). In patients with mild signs of cervical myelopathy (not meeting the above criteria for surgery), nonsurgical treatment is reasonable. This recommendation is supported by the results of a small, but otherwise well-designed, randomized trial in- Figure 2. Anterior cervical diskectomy (Panel A) can be performed without spinal fusion, although more commonly a fusion (using a variety of biologic and synthetic materials) is performed to prevent disk collapse and kyphosis. As illustrated in the figure, this is commonly accompanied by anterior fixation of a plate to facilitate early return to normal activity.
50 mcg flonase otc. My God this allergies 😷!.
Use of non-opioid medications was also reduced but was statistically insignificant allergy symptoms baby cheap 50 mcg flonase. The authors concluded that in patients treated with intrathecal opioids allergy treatment by homeopathy cheap flonase 50mcg online, the addition of bupivacaine may improve outcomes. Good to excellent satisfaction was reported in 29 of the 30 implanted patients, activities of daily living were improved in 26 patients and 12 patients were able to return to full-time employment. A study by Atli et al (2115) retrospectively examined charts of 57 patients, 55 with non-cancer pain. Considering that the pain from a recent vertebral fracture may normally improve after 6 months to a year, the contribution of the pump implant to the reduction in pain scores in this study is unclear. In addition, vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are less expensive options compared to an intrathecal infusion pump. Thus, intrathecal morphine for vertebral fractures may have limited applications to patients who are not candidates for vertebral augmentation procedures. A Canadian study also demonstrated the cost effectiveness of intrathecal infusion devices. Kumar et al (2012) looked at the cost of implanting a programmable drug delivery pump versus conservative treatment of chronic pain. High initial costs of equipment required for intrathecal drug delivery were recovered by 28 months. After this time, managing patients with conservative treatments became more expensive for the remainder of the follow-up period. This is an important finding and may help justify the initial cost of the implantable pump system. Overall, all the observational studies have shown a long-term benefit from intrathecal infusion devices used for chronic non-cancer pain, as illustrated in Table 42. While the vast majority of complications are minor, some serious complications can occur (27,225,506,2077,20992100,2102-2154). An increased mortality rate in patients with non-cancer pain receiving intrathecal opioid therapy (mortality rate of 0. Other serious complications include granuloma formation that may be related to the amount and concentration of opiates, mostly morphine and hydromorphone (2138,2148-2152). Surgical interventions in these cases are rare (2153) as most cases improve with weaning off of the intrathecal opiate, replacing it with preservative-free saline, which has been shown to reverse the course leading to resolution of the granuloma (2148,2149). Intrathecal infusion systems for long-term management of chronic non-cancer pain: An update of assessment of evidence. The purpose of the described algorithmic approach is to provide a disciplined approach to the use of spinal interventional techniques in managing spinal pain. This approach includes evaluation, diagnostic, and therapeutic approaches, which in turn avoid unnecessary care as well as poorly documented practices. Furthermore, with space constraints, comprehensive initial evaluations and all the findings are not provided. Appropriate history, physical examination, and medical decision-making are essential to the provision of appropriate documentation and patient care. Not covered in this algorithm are socioeconomic issues and psychosocial factors that may be important in the clinical decision-making process. A comprehensive and complete evaluation will assist in complying with regulations, providing appropriate care, and fulfilling an algorithmic approach. For confirmed disc herniation, radiculitis, or spinal stenosis, diagnostic approaches depend on symptoms, signs, and radiologic evaluation. Thus, this algorithmic approach for chronic low back pain without disc herniation is based on the best available evidence on the epidemiology of various identifiable sources of chronic low back pain. Facet joint pain, discogenic pain, and sacroiliac joint pain have been proven to be common causes of pain with proven diagnostic techniques (8,11,13,15,17,33,36-38,644,1250,1325,1469,1471,2155). If there is evidence of radiculitis, spinal stenosis, or other demonstrable causes resulting in radiculitis, one may proceed with diagnostic transforaminal or therapeutic epidural injections (8,644,2155). Otherwise, an algorithmic approach should include diagnostic interventions with facet joint blocks and sacroiliac joint injections, followed by discography. At the present time, lumbar discography time suffers from significant controversy with fair evidence (36). In contrast, there is good evidence to support facet joint nerve blocks in the diagnosis of lumbar facet joint pain and sacroiliac joint injections (11,17).
References:
- http://www.dce.ndsu.nodak.edu/dceweb/dataimports/The_Barcelona_Way__Unlocking_the_DNA_of_a_Winning_Culture_(_PDF_Drive_).pdf
- https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/1013_investing_in_young_children_haskins.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5216.pdf
- https://www.smith-nephew.com/documents/anz/aus/awm%20catalogue/sn13577%20wound%20management%20catalogue%20anz.secure.pdf
- http://whcc.labiomed.org/book/2.3.8%20Complications%20Actinomycosis.pdf