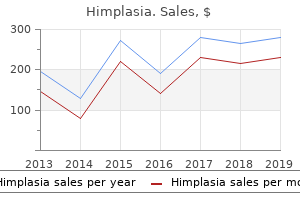
Himplasia
"30 caps himplasia visa, herbals definition."
By: Brent Fulton PhD, MBA
- Associate Adjunct Professor, Health Economics and Policy

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/brent-fulton/
Involvement of the oculomotor nucleus will produce ipsilateral paralysis of the levator palpebrae superioris; the superior herbals information himplasia 30caps overnight delivery, inferior herbals product models purchase 30caps himplasia fast delivery, and medial rectus muscles; and the inferior oblique muscle. Malfunction of the parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotor nerve produces a dilated pupil that is insensitive to light and does not constrict on accommodation. Involvement of the trochlear nucleus will produce contralateral paralysis of the superior oblique muscle of the eyeball. Thus, it is seen that involvement of one or both of these nuclei, or the corticonuclear fibers that converge on them, will cause impairment of ocular movements. Blockage of the Cerebral Aqueduct the cavity of the midbrain, the cerebral aqueduct, is one of the narrower parts of the ventricular system. Normally, cerebrospinal fluid that has been produced in the lateral and third ventricles passes through this channel to enter the fourth ventricle and so escapes through the foramina in its roof to enter the subarachnoid space. In congenital hydrocephalus, the cerebral aqueduct may be blocked or replaced by numerous small tubular passages that are insufficient for the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid. When the cerebral aqueduct is blocked, the accumulating cerebrospinal fluid within the third and lateral ventricles produces lesions in the midbrain. The presence of the oculomotor and trochlear nerve nuclei, together with the important descending corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, will provide symptoms and signs that are helpful in accurately localizing a lesion in the brainstem. B: Weber syndrome involving the oculomotor nerve and the crus cerebri following occlusion of the blood supply to the midbrain. C: Benedikt syndrome involving the red nucleus and the medial lemniscus following occlusion of the blood supply to the midbrain. There is ipsilateral ophthalmoplegia and contralateral paralysis of the lower part of the face, the tongue, and the arm and leg. The eyeball is deviated laterally because of the paralysis of the medial rectus muscle; there is drooping (ptosis) of the upper lid, and the pupil is dilated and fixed to light and accommodation. A 6-month-old boy died with hydrocephalus and a myelocele in the lower thoracic region. The lower part of the medulla oblongata extended inferiorly through the foramen magnum into the vertebral canal as far as the third cervical vertebra. The lower four cranial nerves were longer than normal, and the upper cervical nerve roots ascended to reach their exit from the vertebral canal. The cerebellum on the left side extended inferiorly through the foramen magnum to the third cervical vertebra, where it was adherent to the spinal cord. A 68-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with the sudden onset of severe dizziness (vertigo), hiccups, and vomiting. He also complained of a hot, painful sensation in the skin of the right side of the face. The patient also showed drooping of the right upper eyelid (ptosis), sunken right eye (enophthalmos), and a constricted right pupil (myosis). When asked to protrude his tongue straight out of his mouth, the patient tried to do so, but the tip of the tongue pointed to the right side. There was evidence of impairment of pain and temperature sensation in the trunk and extremities on the left side. A pathologist, while exploring the posterior cranial fossa during an autopsy, was endeavoring to determine where the 9th, the 10th, and the cranial part of the 11th cranial nerves emerged from the hindbrain. A 10-year-old girl was taken to a physician because her mother had noticed that the right half of her face was weak and did not appear to react to emotional changes. It was noted also that her mouth was pulled over slightly to the left, especially when she was tired. The mother had first noticed the facial changes 3 months previously, and the condition had progressively worsened.
Palatine tori are frequently observed during the middle phase of life than at a younger and older age herbals for liver effective 30 caps himplasia. In the present study as age has not been considered as variable and so differences in frequency of palatine torus with age cannot be ascertained herbals names cheap 30caps himplasia overnight delivery. Though, in the present study reliability of palatine torus in sex determination has been found to be 48. Thus, before conducting sex determination studies of palatine torus, age grouping should be done in prior race determined samples. The present study suggests that there exists no association between palatine torus development and maxillo-alveolar index but Woo1 inferred from his studies that the large type of torus has smallest palatal index and the small type has largest palatal index. P Raghvan, Senior Research Associate Scientist, Australian National University, for giving us training in studying the cranial morphological traits and biometric methods. Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of interest in the present research paper Source of Funding: No funds were required as the research was conducted in the Department of Anatomy and Forensic Medicine, Government Medical College, Patiala on dry skulls which were available in Departments only. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of oral tori in 1520 Chulalongkorn university dental school patients. The relationship of temporomandibular joint disorders with bony exostosis in the oral cavity. Morphology and incidence of torus palatinus and mandibularis in Brazilian Indians. Variations of the prominences of the bony palate and their relationship to complete dentures in Korean skulls. Pakistan Oral and Dental Journal 2007; 27(1): 89-92 Derar Al-Sebaie and Mashoor Alwrikat. Prevalance of torus palatinus and torus mandibularis in the Split-Dalmatian County, Croatia. A re-evaluation of estimation based on measurements of stature taken during life and of long bones after death. Forensic osteology: Advances in the identification of human remains in Forensic implications of skeletal pathology: sex. Drowning suffocation causes a lack of oxygen, resulting death in only a few minutes. An exception to this rule appears in victims who have been suddenly and rapidly submerged into ice-cold water. Drowning is the 3rd leading cause of unintentional injury death, accounting for 7% of all injury-related deaths1. For children, it is the second leading cause of accidental death in school going children and the number one cause for preschoolers2. The medico-legal investigation of bodies found in water focuses on victim identification, evaluation of post mortem submersion time, and determination of the cause and manner of death. In addition to drowning, injuries, intoxications, or natural conditions are all among the potential causes of death in bodies found in water or the factor that may have contributed to the fatal outcome. Emphasis is placed on certain pitfalls for the unwary, which if not taken cognizance of, may lead to a miscarriage of justice. Before conducting autopsy, the identity was established by his parents who gave the history that the boy was a good swimmer and took 150 Rs for purchasing books, but went to the swimming pool of a hotel along with his friends where this mishap took place. Autopsy findings External findings Dead body of 12 year old average built boy, wheatish in complexion and was naked with only blue colored underwear. Eyes were semi open, pupils dilated and fixed, mouth semi open and dried yellow 128 Medico-Legal Update, January-June 2015, Vol. Internal Findings On opening, the trachea was full of froth which was fine, non collapsble, lathery, tenacious and white in color. Both the kidneys showing severe diffuse haematoma on its surface in sub-capsular space. Stomach containing about 500cc of light yellow watery semi digested food material. Cause of death was given as asphyxia as a result of ante-mortem drowning and duration of death was within 6 hrs since postmortem examination.
It originates from the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries at the base of the femoral neck and the extracapsular arterial ring herbalstarcandlescom generic himplasia 30 caps otc. Any disruption of the femoral neck is likely to interfere with the blood supply of the head of the femur mobu herbals extracting balm himplasia 30caps overnight delivery, thus causing avascular necrosis, which occurs in more than one-third of displaced femoral neck fractures. Nonunion, the other complication of femoral neck trauma, is related to the presence of synovial fluid, which bathes the fracture site. It is more difficult for the bone to heal in this environment, and it is difficult to reduce the fragments anatomically. No displaced femoral neck fracture, therefore, can heal when treated nonoperatively. Fractures of the neck of the femur are classified into nondisplaced and displaced. Nondisplaced (so-called impacted valgus fractures) are inherently stable and may heal without surgery. These fractures, nondisplaced or valgus impacted, will normally heal, and the patient is allowed to get up and move about with partial weight-bearing until healing takes place; usually this occurs in 6 to 8 weeks. When a fracture of the neck of the femur is displaced, an effort may be made to do a closed reduction in the operating room, which must be confirmed radiographically. Skeletal Trauma 71 more advantageous to avoid the possibility of nonunion, avascular necrosis, and an invalid life for several months by removing the head of the femur and replacing it with an endoprosthesis. This device enables patients to walk the day after the operation bearing most of their body weight. These prostheses can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years, and, therefore, in a young person every effort should be made to save the native femoral head. If a reduction of the fracture is performed and avascular necrosis or a nonunion occurs, a total hip replacement is the usual solution. Intertrochanteric Fractures Intertrochanteric fractures occur at or below the line between the greater and lesser trochanter and lie outside the capsule. On physical examination in the emergency room, these patients, similar to those with the displaced femoral neck fractures, will manifest shortening and external rotation. If an attempt were made to treat such a fracture without operative intervention, the patient would likely not survive protracted bed rest. Such a patient is likely to die of pneumonia, pulmonary emboli, bedsores, urinary tract infections, or the emotional damage that occurs in an old person when bedridden. Review of the X-rays allows one to determine whether the fracture is stable or unstable. When the proximal femur is fractured into three to four separate fragments, and especially if the lesser trochanter with its posteromedial cortex is one of these fragments, the fracture is unstable. In these cases, fixation must be rigid, and full weight-bearing often cannot be allowed for quite a few months. Because of the high incidence of implant failure seen with unstable fractures, other Figure 2-18. Skeletal Trauma 73 solutions have been sought, one of them being a prosthetic replacement of all the fragments that are damaged. This procedure is a larger operation than the endoprosthesis for a femoral neck fracture and, therefore, is not often done. Healing in the intertrochanteric fracture usually proceeds well, assuming the fixation is adequate. Subtrochanteric Fractures Subtrochanteric fractures occur through an area below the lesser trochanter and are not quite as rapid to heal as the intertrochanteric injuries. In the elderly, they are the result of severe osteoporosis or a pathologic process in the subtrochanteric area. Fixation is either by a standard hip screw, as described for the intertrochanteric fracture, but with a longer side plate or an intramedullary nail with proximal and distal locking screws. In children, intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures are generally treated in traction, whereas the very rare fracture of the femoral neck, even in a child, must be surgically treated in an effort to achieve union and avoid avascular necrosis.
Himplasia 30 caps fast delivery. R&G Fresh Herbs - Herb Storage Tips - Freezing Herbs.
References:
- https://www.aohp.org/aohp/portals/0/Documents/Conference/B019%20Rielly%20revised.pdf
- https://www.fanconi.org/images/uploads/other/FA_Guidelines_4th_Edition_Revised_Names_in_Appendix.pdf
- https://www.drlamcoaching.com/downloads/Beating-Cancer-with-Natural-Medicine.pdf
- https://www.lls.org/sites/default/files/file_assets/FS14_Myelofibrosis_Fact%20Sheet_Final9.12.pdf