Propecia
"Cheap propecia 1 mg without a prescription, hair loss cure 360."
By: Paul J. Gertler PhD
- Professor, Graduate Program in Health Management

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/paul-gertler/
Deicing Fluids Deicing fluids are composed of methyl anti hair loss cream safe 1 mg propecia, ethyl hair loss hormones buy propecia 1mg with visa, and isopropyl alcohols. When they are absorbed after ingestion, intoxication with methyl effects is produced. Organophosphates inhibit the enzyme cholinesterase and the toxic effects are related to the resulting increase in endogenous acetylcholine at the synaptic sites. Monitoring enzyme activity not only can serve as a measure of acute toxicity, but also can be used to monitor occupational exposure (remove from exposure if enzyme activity decreases more than 25 percent from preexposure levels). The time of onset of symptoms after toxic exposure can be very rapid, but rarely longer than a few hours. More severe exposure produces coughing, wheezing, and increased bronchial secretions. Weakness and fatigability lead to twitching, fasiculations, and eventual respiratory paralysis. Atropine does not reverse phosphorylation of cholinesterase, but blocks the effect of acetylcholine. Beryllium produces pulmonary and systemic granulomatous disease requiring exposure over months to years. Beryllium pneumonitis acts like the classic pneumonitis where the X-ray looks worse than the patient. The pneumonia may appear up to six weeks after a beryllium exposure of 1 to 20 days duration and can require up to six months to resolve. Beryllium pulmonary granulomatosis is the most feared form of reaction, appearing weeks to years after the initial exposure and closely resembles sarcoid in that it is not merely pulmonary in focus. The diagnosis of beryllium pulmonary granulomatosis is made mostly by history and by exclusion, since there is no reliable method for beryllium assay, and the X-ray is nonspecific. Overall mortality from this syndrome has been estimated to be as high as 30 percent and as low as 2 percent. Modern technology has produced new uses of beryllium in nuclear reactors, electronic equipment, guidance and navigation systems, rocket parts, and heat shields. A symptom-free period is followed in 4 to 10 hours with dyspnea, cough, chest tightness, chest pain and burning. Chronically, cadmium can cause pulmonary fibrosis, liver and kidney damage, and cancer of the lung and the prostate. Cadmium in the Navy is found in electroplating, as a stabilizer in plastics, and as a component in nickel-cadmium batteries. Chromium exposure generally results in cough, wheezing, pain on inspiration, fever, weight loss, and possible chemical pneumonitis. Only the hexavalent form is dangerous and causes both skin ulcers and respiratory ulcers. In the Navy, chromium is found in chrome plating and as a paint primer (corrosion resistance). It is a common ion found in rework facilities which causes severe ulcers which are slow to heal. Lead poisoning is essentially a chronic disease caused by the gradual accumulation of a significant body burden. One of the most important sites of the toxic action of lead is the inhibition of the heme biosynthetic pathway. Efforts must be made to keep the blood lead level less than 40 micrograms per 100 ml. The "lead caper": Colic, Arthralgia, Polyneuritis, Encephalopathy, Red blood cell stippling and anemia. Within the Navy, lead-based paint is very common and sanding can cause airborne exposure. Heating, grinding, spraying, or burning may result in emission of biologically active forms of lead. Consideration of lead exposure is important in the demolition of ships because of lead-based paint. Nickel Nickel is an elemental metal of little toxicity as the metal, but with many toxic compounds.
Besides the emerging nerve root and dorsal root ganglion hair loss blood tests discount 1 mg propecia otc, the intervertebral foramen contains fat and foraminal veins hair loss 6 months after hair transplant purchase 5mg propecia fast delivery. Pedicular level: the section passes through the upper half of the vertebral body, the pedicles, transverse processes, upper neural arch and spinous process. Infrapedicular level: the section passes through the lower half of the vertebral body and upper half of the intervertebral foramina containing the dorsal root ganglions, additionally the facets with their joint capsules and the flaval ligaments, and the lower half of the spinous process. Disk level: the section passes through the intervertebral disk and lower half of the intervertebral foramen, containing mainly fat and veins; also through the lower half of facets, joint capsules and flaval ligaments. Mid-sagittal section: this section shows the spinal cord and conus medullaris well, also the sagittal dimensions of the spinal canal and the epidural fat. Lateral sagittal section: this section provides a good sagittal image of the intervertebral foramen. S Functional Anatomy When the spine moves from flexion or kyphosis to extension or lordosis, this has an effect upon intraspinal dimensions and structures. As lordosis increases, the spinal canal shortens due to the position of the axis of movement being located within the vertebral body, anterior to the canal. The disk bulges backward into the 1700 Spinal Cord canal and the flaval ligaments also bulge inward, thus narrowing the canal at the disk level. These are normal phenomena but in cases with narrowing or stenosis of the canal, these posture-induced changes may be sufficient to cause cauda equina compression with neurogenic claudication in the lumbar spine, or aggravation of spinal cord compression in the cervical region. Degenerative Disease Intervertebral Disk Degenerative changes of the disk commence in late adolescence, with dehydration of the nucleus pulposus and fissure formation in the annulus fibrosus. Such changes can also occur in normal aging, and a convincing relationship with backache or sciatic pain has not been established. With nuclear dehydration goes decrease in disk height, which in turn leads to circumferential bulging of the annulus, also into the spinal canal ("bulging disk"). When a weakened annulus fibrosus ruptures, material from the nucleus pulposus may be displaced into the spinal canal ("herniated disk"; "herniated nucleus pulposus"). Nomenclature is as follows: when the height of the herniated material does not exceed the height of the parent disk, this is called a protrusion. When the herniated mass is higher than the parent disk, it is called an extrusion. Bulging disks usually do not cause nerve root compression, unless there is associated narrowing of the spinal canal. Protruded disks are frequently asymptomatic, extruded disk fragments usually compress the root. Extruded material may migrate some distance to compress a root in the intervertebral foramen or the lateral recess. A compressed nerve root undergoes inflammatory changes, which in the lumbar region lead to the clinical symptom of sciatica: pain irradiating into the dermatome of the leg supplied by the affected root. Sensory loss in the dermatome may ensue, as well as muscle weakness and decreased tendon reflexes. A large extrusion may cause a cauda equina syndrome with severe neurologic deficit including bladder paralysis. In the cervical spine, root compression by disk herniation causes brachialgia: pain irradiating into a dermatome of the arm. Contrast injection is sometimes useful in these cases to identify postoperative scarring. Even in unoperated patients, extruded and migrated disk material will frequently demonstrate peripheral contrast enhancement. Spinal Narrowing Developmental spinal stenosis is an uncommon shallowness of the spinal canal seen especially frequently in achondroplasia. Lumbar stenosis leads to neurogenic claudication; irradiating pain and numbness in the legs on walking and standing, relieved by sitting and squatting, caused by chronic posture-dependent cauda equina compression. Much more frequent is degenerative narrowing of the lateral region of the spinal canal due to hypertrophy of the facets and flaval ligaments in spondylarthrosis.
Discount 1mg propecia with visa. Homeopathic Medicine For Hair Fall And Regrowth || How to Stop Hair Fall Alopecia & Baldness.
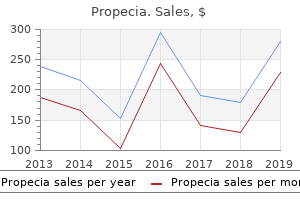
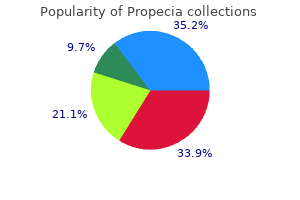
Since each injury is different as to its level and severity hair loss 7 keto quality 5mg propecia, the information is provided in general terms hair loss cure protein discount propecia 1 mg mastercard. Acute Management the first few hours are critical after a spinal cord injury, as life-saving interventions and efforts to limit the severity of the injury take precedence. Ideally, a spinally injured person should be transported to a Level I trauma center for multidisciplinary expertise. If cervical spine injury is suspected, the head and Paralysis Resource Guide 174 3 neck are immediately stabilized. Cooling has been tested in clinical trials and appears promising, but protocols for temperature, duration, etc. Once a person reaches the acute hospital, several basic life-support procedures may occur. Tracheostomy or endotracheal intubation is often done even before location of injury is established. Early surgery (within hours of injury) to decompress or align the spinal canal is often done. Evidence from animal studies supports this as a means to improve neurologic recovery but the timing of this intervention is subject to debate; some surgeons wait several days to allow swelling to subside before decompressing the cord. Spinal cord injuries commonly lead to paralysis; they involve damage to the nerves within the bony protection of the spinal canal. The most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction is trauma (including motor vehicle accidents, falls, shallow diving, acts of violence, and sports injuries). Damage can also occur from various diseases acquired at birth or later in life, from tumors, electric shock, and loss of oxygen related to surgical or underwater mishaps. The spinal cord does not have to be severed in order for a loss of function to occur. For cervical fractures, the spine is often stabilized by a bone fusion, using grafts from the fibula (calf bone), tibia (shin bone) or iliac crest (hip). To stabilize spinal bones, a spinal fusion might be done, using metal plates, screws, wires and/or rods and sometimes small pieces of bone from other areas of the body. A spinal cord injured patient will typically encounter several external devices, including braces, traction pulleys, skull tongs, turning frames, molded plastic jackets, collars and corsets. Bracing devices are often used early on; they allow vertebral bones to heal but allow patients to be up and around, protecting them from the effects of bed rest. Classifying the Injury: Once physicians determine the level and extent of the injury, the patient will also undergo a thorough neurological examination. This looks for signs of sensation, muscle tone and reflexes of all limbs and the trunk. These folks are most likely to be ventilator dependent and typically need 24-hour attendant care with total assistance with bowel and bladder management, bed mobility, transfers, eating, dressing, grooming, bathing and transportation. They can power an electric wheelchair and can be independent communicators with the right equipment; they need to be able to explain everything an assistant needs to know about their care. May be able to breathe without a ventilator, otherwise, similar profile as the C1-3 group: total assistance needed for all tasks except power wheelchair use. These people can eat independently if meals are set up for them but still need some assistance for grooming, bed transfers and dressing. Some people with a C5 injury can drive a vehicle with the right specialized equipment and training. No wrist flexion or hand movement but can push a manual chair and do weight shifts. Personal care needed but on a limited basis; getting up in the morning, grooming, going to bed. Level C7/8: Paralysis of trunk and legs but with greater arm and hand dexterity, including elbow, wrist and thumb extension. Some compromised vital capacity but independent for almost all functional self-care activities. Level T10-L1: Paralysis of legs but good trunk stability; intact respiratory system. Level L2-S5: Partial paralysis of legs, hips, knees, ankles and feet, good trunk support.
T h e s e t h r e e p r o t e i n s a r e p r e s e n t hair loss 8 months after giving birth purchase propecia 5mg online, i n the o r g a n i ze r (p r i mi t i v e n o d e) hair loss guinea pig purchase propecia 1 mg with visa, n o t o c h o r d, a n d p r e c h o r d a l me s o d e r m. T h e y n e u r a l i ze e c t o d e r m a n d c a u s e me s o d e r m t o b e c o me n o t o c h o r d a n d p a r a xi a l me s o d e r m (d o r s a l i ze s me s o d e r m). H o w e v e r, the s e n e u r a l i n d u c e r s i n d u c e o n l y f o r e b r a i n a n d mi d b r a i n t y p e s o f t i s s u e s. In d u c t i o n o f c a u d a l n e u r a l p l a t e s t r u c t u r e s (h i n d b r a i n a n d s p i n a l c o r d) d e p e n d s u p o n t w o s e c r e t eW N To taa n s F G F. C l o s u r e o f the c r a n i a l n e u r o p o r e o c c u r s a t e g a) a p p r o xi ma t e l y d a y 2 5 (1 8 - t o 2 0 - s o mi t e s t a g e), w h e r e a s the p o s t e r i o r n e u r o p o r e c l o s e s a t d a y 2 7 (2 5 - s o mi t e s t a g e). N e u r u l a t i o n i s the n c o mp l e t e, a n d the c e n t r a l nervous system is represented by a closed tubular structure with a narrow caudal p o r t i o n, t hs p i n a l c o r da n d a mu c h b r o a d e r c e p h a l i c p o r t i o n c h a r a c t e r i ze d b y a e, n u mb e r o f d i l a t i o n s, bt r a i n v e s i c l e(s e eC h a p t e r 1 7 he). T h e p r i mi t i v e s t r e a k 1 a n d p r i mi t i v e n o d e a r e v i s i b lD o r s a l v i e w o f a n 1 8 - d a y p r e s o mi t e e mb r y o. T h e e mb r y o i s p e a r - s h a p e d, w i t h i t s c e p h a l i c r e g i o n s o me w h a t b r o a d e r t h a n i t s c a u d a l e n d. N o t e the p r i mi t i v e C n o d e a n d, e xt e n d i n g f o r w a r d f r o m i t, the n o t o c h o r d. As the n e u r a l f o l d s e l e v a t e a n d f u s e, c e l l s a t the l a t e r a l b o r d e r o r c r e s t o f the neuroectoderm begin to dissociate from their neighbors. A g rB o in e tmoo r p h o g e n e t i c ad en f p r o t e i n s (B M P ss e c r e t e d b y n o n n e u r a l e c t o d e r m, t o g e the r w i t h F G F s, i n i t i a t e s,) the induction process. Crest cells give rise to a h e t e r o g e n e o u s a r r a y o f t i s s u e s, a s i n d i Ta t e e 6n. D o r s a l v i e w o f a l a t e p r e s o mi t e e mb r y o (a p p r o xi ma t e l y 1 9 d a y s). C r e s t c e l l s f o r m a t the t i p s o f n e u r a l f o l d s a n d d o n o t mi g r a t e a w a y f r o m t h i s r e g i o n u n t i l n e u r a l t u b e c l o s u r e i s c C mp lte tre. Af e contribute to a heterogeneous array of structures, including dorsal root g a n g l i a, s y mp a the t i c c h a i n g a n g l i a, a d r e n a l me d u l l a, a n d o tTae rl e i s s u e s (h b t 6. In a s c a n n i n g e l e c t r o n mi c r o g r a p h, c r e s t c e l l s a t the t o p o f the). T hese cells leave the crests of the neural folds prior to neural tube c l o s u r e a n d mi g r a t e t o f o r m s t r u c t u r e s i n the f a c e bl n d n eea 1(, a ue ar c k). S e v e n 5 d i s t i n c t s o mi t e s a r e v i s i b l e o n e a c h s i d e o f the n e u rD o rts a lev i e w o f a B. N o t e the p e r i c a r d i a l b u l g e o n e a c h s i d e o f the mi d l i n e i n the c e p h a l i c p a r t o f the e mb r y D. L a t e r a l v i e w o f a 1 4 - s o mi t e e mb r y o (a p p r o xi ma t e l y 2 5 d a y s). T h e l e f t s i d e o f a 2 5 - s o mi t e e mb r y o a p p r o xi ma t e l y 2 8 d a y s o l d. B y the t i me the n e u r a l t u b e i s c l o s e d, t w o eb i t a td e am a l t h i c k e n i,n tg s c l o err l he o t i c p l a c o d ea n d t h ee n s p l a c o d e s e c o me v i s i b l e i n the c e p h a l i c r e g i o n o f the s l, b e mb r y o F i g. T h e s e p l a c o d e s a l s o i n v a g i n a t e a n d, d u r i n g the f i f t h w e e k, s f o r m t h ee n s e so f the e y e s (s Ce a p t e r 1 9 l eh). In a d d i t i o n, i t g i v e s r i s e t o (s u b c u t a n e o u s g l a n d s, the ma mma r y g l a n d s, the p i t u i t a r y g l a n d, a n d e n a me l o f the teeth. De riv ativ e s of the Me sode rm al Ge rm Lay e r In i t i a l l y, c e l l s o f the me s o d e r ma l g e r m l a y e r f o r m a t h i n s h e e t o f l o o s e l y w o v e n t i s s u e o n e a c h s i d e o f the mi d l i nF i g s e e)7 B y a p p r o xi ma t e l y the 1 7 t h d a y, e (. To g e the r, the s e l a y e r s l i n e (e a a n e w l y f o r me d c a v i t y,i nhr a e m b r y o n i c c a v iwy i c h i s c o n t i n u o u s w i t h the tte, th e xt r a e mb r y o n i c c a v i t y o n e a c h s i d e o f the I e mbrrmo. T h e s e s e g me n t s, k n o w o m ist o m e r e sf i r s t a p p e a r i n the c e p h a l i c Sn a, r e g i o n o f the e mb r y o, a n d the i r f o r ma t i o n p r o c e e d s c e p h a l o c a u d a l l y. E a c h s o mi t o me r e c o n s i s t s o f me s o d e r ma l c e l l s a r r a n g e d i n c o n c e n t r i c w h o r l s a r o u n d the c e n t e r o f the u n i t. In the h e a d r e g i o n, s o mi t o me r e s f o r m i n a s s o c i a t i o n w i t h s e g me n t a t i o n o f the n e u r a l p l a tn e iu rto m e r e s n d c o n t r i b u t e t o me s e n c h y me e n o a i n the h e a d (s e e a p t e r 1 6 F r o m the o c c i p i t a l r e g i o n c a u d a l l y, s o mi t o me r e s Ch).
References:
- https://www.nceedus.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/FEAST-ED-Nutrition.pdf
- https://jmhg.springeropen.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s43042-019-0031-4.pdf
- https://www.veinforum.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Chapter-13-Compression-Therapy-for-Venous-Disorders-and-Venous-Ulceration.pdf
- http://webhome.auburn.edu/~deruija/prostaglandins_2002.pdf