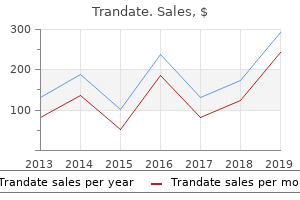
Trandate
"Buy trandate 100 mg visa, blood pressure and heart rate."
By: Paul J. Gertler PhD
- Professor, Graduate Program in Health Management

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/paul-gertler/
Lower miR-99a/100 expression indeed directly correlated with radio-resistance of prostate cancer cell lines arrhythmia forum generic 100mg trandate free shipping. A sub-cell population of expanded Human Oral Mucosal Epithelial biopsies shows stem cell characteristics with differentiation potential to ocular surface cells pulse pressure stroke 100 mg trandate overnight delivery. Tissue engineering of these cells could be useful for regeneration of human ocular surface tissues. We studied the histopathological alterations (number, size and characteristics of the tumors in the colon). The exponential dose-response relationship demonstrates the association between the number of transplanted cells and the resulting normalization of colon mucosa. It may suggest about huge role of immune system in stem cells modulation of cancer cells. In this study, we demonstrated the similarity of placentaderived cell culture to both mesenchymal and trophoblast stem cells. The extent of lung fibrosis and inflammation, and macrophage polarity and function were measured 7 and 14 days later. And polarization of macrophages occurs as a consequence of this cellular interaction. To explore the mechanisms involved in midgut patterning, we dissected the transcriptional regulatory elements of Nephrocan (Nepn), the earliest known midgut specific gene in mice. We observed that Nepn expression is dramatically reduced in Sox17-/- and Raldh2-/- embryos compared to wild-type embryos. We further show that Nepn is directly regulated by Sox17 and the retinoic acid receptor via two enhancer elements located upstream of the gene. In FoxH1-/- embryos in which Nodal signaling is reduced, the Nepn expression domain is expanded into the anterior gut region suggesting that Nodal signaling can modulate expression in vivo. A balance of Nodal/Activin signaling regulates the anterior boundary of the midgut expression domain. Efforts at chemotherapy and surgical resection have not appreciably altered survival rates, and therefore much hope is placed on detecting and treating less aggressive precursors of this disease. These findings define a stem cell target for preemptive therapies of a precancerous lesion. In this study, we isolated the dermal cells from skin of newborn of C57/B6 mice and investigated the cell characteristic of multipotency. Much of what is known about Wnt signaling and stem cells comes from studies on the intestine, where Wnt/catenin signaling is essential for maintenance of their intestinal crypts and allows intestinal stem cells to maintain long-term organoid cultures in vitro. In skin, this often leads to scar formation with loss of associated appendages including hair follicles. Since hair follicles are composed of various distinct epithelial and mesenchymal cells in an organized three-dimensional structure, direct conversion of cells into a single cell type is not able to regenerate a functional hair follicle. To regenerate functional skin, we asked whether hair follicle regeneration can be facilitated by defined extracellular factors. We found that tissue extraction from a specific developmental stage was able to induce hair follicle neogenesis from non-follicular cells. Adult fibroblasts with short-term exposure to the extraction in vitro were able to induce hair follicle neogenesis from keratinocytes when they were transplanted back in vivo. Hence, such pro-regeneration effect worked through regulating adult fibroblasts, but not epithelial cells, to initiate their cross-talk with keratinocytes for hair follicle neogenesis. In further analysis, we discovered defined extracellular factors that together were sufficient to initiate hair follicle neogenesis. Therefore, organ neogenesis can be facilitated by creating a pro-regeneration environment with defined extracellular factors. Identification of such factors can be combined with other schemes for functional regeneration of tissues and organs. Despite their importance for human survival and quality of lives, little is known about sweat gland development at the molecular level. Like other skin appendages, hair follicles or mammary glands, they originate from epidermal progenitors. Using lineage tracing, we identify multipotent progenitors in the sweat duct that transition to unipotency after developing the sweat gland. Physiological cell death programs promote the rapid removal of excess or dysfunctional cells without eliciting harmful effects on surrounding healthy tissue. Studying this process under physiological conditions in vivo has been difficult due to the rapid rate by which dead cells are normally removed as well as the counterbalancing effects of proliferation with the same tissue.
Intravenous administration is more reliable arrhythmia technologies institute order trandate 100mg otc, and the maximum total dose of 200 mg is reported to produce significantly lower pain scores and no difference in maternal or neonatal complications blood pressure medication pregnancy quality 100 mg trandate. The adverse effects of pethidine and its active metabolite norpethidine on the fetus may-in rare instances-need to be reversed by an opioid antagonist. Onset time and context-sensitive half-life of all available opioids are comparable, and so the potential to induce Pharmacological Management of Pain in Obstetrics Table 1 Relative infant dose and clinical significance of selected analgesic agents Drug Ibuprofen Ketorolac Naproxen Relative Infant Dose (%) 0. Milk concentrations low; plasma concentrations low-to-undetectable in infants; caution with chronic administration. The use of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) in single doses should not pose any significant risks to the suckling infant. The use of pethidine (meperidine) in the perinatal period is increasingly controversial. Although the drug is used commonly in obstetrics, such use is gaining disfavor as more sedation is reported in newborns. When administered to mothers, the drug has been found to produce neonatal respiratory depression, decreased Apgar scores, lower oxygen saturation, respiratory acidosis, and abnormal neurobehavioral scores. In women receiving doses varying from 50 to 400 g intravenously during labor, the amount found in milk was generally below the limit of detection (<0. The possible advantages must be balanced against higher cost and possible cardiovascular risks, which should be minimal with shortterm use in healthy young women. Katarina Jankovic breastfeeding because of negligible maternal plasma levels achieved. A randomized study that compared spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean with or without the use of postoperative extradural continuous bupivacaine found that the continuous group had lower pain scores and a higher volume of milk fed to their infants. In general, if treatment of a lactating mother with an analgesic drug is considered necessary, the lowest effective maternal dose should be given. Moreover, infant exposure can be further reduced if breastfeeding is avoided at times of peak drug concentration in milk. This dose is probably too low to affect a breastfeeding infant, but this drug is a strong opioid, and some caution is recommended. A variety of different drug classes are used in obstetrics when regional techniques and opioids are not available. Above all, a single small dose of benzodiazepines may be used (mainly midazolam or diazepam). In prodromal and early stages of childbirth, barbiturates (secobarbital or pentobarbital) may be a choice, and in experienced hands ketamine or S-ketamine may be helpful. John Snow provided for her eighth childbirth (Prince Leopold) the newly developed chloroform anesthesia with an open-drop Table 2 Use of analgesics in pregnancy Medication Opioids and Opioid Agonists Meperidine Morphine Fentanyl Hydrocodone Oxycodone Propoxyphene Codeine Hydromorphone Methadone Nonsteroidals Diclofenac Etodolac Ibuprofen Indomethacin Ketoprofen Ketorolac Naproxen Sulindac Aspirin Full-strength aspirin Low-dose (baby) aspirin Salicylates Acetaminophen Salicylate-Opioid Combinations Acetaminophen-codeine Acetaminophen-hydrocodone Acetaminophen-oxycodone Acetaminophen-propoxyphene 1 1 1 2 Widely used for treatment of acute pain 1 Widely used 4 1 Full-strength aspirin can cause constriction of the ductus arteriosus Low-dose (baby) aspirin is safe throughout pregnancy 4 4 2/4 2/4 4 4 4 4 Both ibuprofen and indomethacin have been used for short courses before 32 weeks of gestation without harm; indomethacin is often used to arrest preterm labor Associated with third-trimester (after 32 weeks) pregnancy complications: oligohydramnios, premature closure of ductus arteriosus 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 3 Almost all cause respiratory depression in the neonate when used near delivery Used for treatment of acute pain: nephrolithiasis, cholelithiasis, appendicitis, injury, postoperative pain Neonatal narcotic withdrawal is seen in women using long-term opioids Risk Comments 1 = Primary recommended agent 2 = Recommended if currently using or if their primary agent is contraindicated 3 = Limited data to support or prescribe use 4 = Not recommended. Later on, other inhalation ("volatile") agents such as halothane also came into use. The safety of this technique is that the parturient will be unable to hold the mask if she becomes too drowsy, and thus will cease to inhale the anesthetic. The analgesia is considered to be superior to opioids, but less effective than epidural analgesia. Although there are data on maternal desaturation, recent studies have not demonstrated any adverse effects on mothers or neonates. Absolute contraindications include patient refusal, allergy (although "true" allergy to local anesthetics is rare), coagulopathy (to avoid spinal/epidural hematoma; negative history is considered sufficiently effective to identify patients at risk), skin infections at the site of needle entry (to avoid epidural abscess formation), hypovolemia (to avoid profound hypotension from the sympathetic block that comes with epidural analgesia of the lumbar and sacral segments), and increased intracranial pressure (herniation of the cerebral contents through the foramen magnum with distal pressure loss after dural puncture). What is a simple and effective regional anesthesia method for the second stage of labor that is easy to learn and may be applied by the non-anesthetist? The pudendal nerve block is useful for alleviating pain arising from vaginal and perineal distension during the second stage of labor. They are sometimes effective in early labor, but they usually need supplementation with a local anesthetic as labor progresses.
Buy trandate 100 mg online. This Garlic Trick Kills Your High Blood Pressure.
Monitoring serum ferritin may be useful lidocaine arrhythmia best 100 mg trandate, aiming to decrease ferritin levels to less than 1000 mcg/L blood pressure 7850 purchase 100 mg trandate overnight delivery. The availability of iron chelators, such as deferoxamine266 and deferasirox,267-269 provide potentially useful drugs to more readily treat iron overload. A third oral chelating agent, deferiprone, was approved (October 2011) in the United States for the treatment of patients with transfusional iron overload due to thalassemia when current chelation therapy is inadequate. The prescribing information for deferiprone contains a black-box warning pertaining to risks for agranulocytosis, which can lead to serious infections and death. As mentioned above, a black-box warning was added to the prescribing information for deferasirox. The relationship of these episodes to treatment with deferasirox has not yet been established. However, it is recommended that patients on deferasirox therapy be closely monitored. Monitoring should include measurement of serum creatinine and/or creatinine clearance and liver function tests prior to initiation of therapy and regularly thereafter. Deferasirox and deferoxamine should be avoided in patients with creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min. Specifically, the study patients had chronic kidney failure; were receiving radiation therapy for various malignancies, including head and neck cancer, advanced breast cancer, lymphoid cancer, or non-small cell lung cancer; were patients with cancer not receiving chemotherapy; or were orthopedic surgery patients. Clinical trials with other experimental agents that are reportedly capable of increasing hemoglobin levels should be explored in patients with disease that is not responding to standard therapy. Some patients were enrolled in a dose-escalation cohort (n = 27) receiving luspatercept once every 21 days at doses ranging from 0. Other patients enrolled in the dose-expansion cohort (n = 31) received luspatercept doses ranging from 1. Although the optimal duration of therapy with AzaC has not been defined, some data suggest that continuation of AzaC beyond first response may improve remission quality. Further improvement was seen in patients who received AzaC earlier in the course of disease, suggesting that the drug prolonged the duration of stable disease. Ninety percent of the responses occurred prior to cycle 6 with a median number of cycles to first response of 3. The median remission duration was 20 months with a median survival time of 22 months. Alternate dosing regimens using lower doses of decitabine administered in an outpatient setting are currently being evaluated. However, these agents should not be used in lieu of early transplantation or to delay transplantation until loss of response or disease progression. The minimum number of courses prior to considering the treatment a failure should be 4 courses for decitabine or 6 courses for AzaC. As discussed earlier, the optimal duration of therapy with hypomethylating agents has not been well-defined and no consensus exists. Modifications should be made to the dosing frequency for individual patients in the event of toxicity. The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events included myelosuppression (neutropenia, 55%; thrombocytopenia, 44%), which often required treatment interruption or dose reduction. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was reported in 77%, 75%, and 16% of patients and thrombocytopenia occurred in 37%, 38%, and 2% of patients in the lenalidomide 5-mg, 10-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Other independent factors associated with a decreased risk of death were female sex, higher hemoglobin levels, and higher platelet counts. A 50% or greater reduction in transfusion requirement was noted in an additional 37 patients (17%), yielding an overall rate of hematologic improvement of 43%.
Each of these efforts have been accomplished by members who were trained in Orofacial Pain and Neuroscience arteria cerebral media generic trandate 100mg with visa. Thus blood pressure of 140 90 cheap 100mg trandate free shipping, there has been general recognition by leaders in dentistry that Orofacial Pain is a distinct field not incorporated in any of the other specialties. As indicated, diagnosis and treatment of temporomandibular disorders is not exclusive to the Orofacial Pain specialty or programs. Competency in recognizing problems arising during or following dental treatment, and either treating them directly or by referral is an essential skill. The Orofacial Pain specialty stands alone in requiring advanced training and clinical competency in treatment of the whole spectrum of orofacial pain disorders. This is important to the operation and success of dental schools, and to the community of Dentistry. Recognition of trained specialists in Orofacial Pain in dental schools (as opposed to management of acute dental pain problems) is becoming important to affiliated hospital and medical center programs in knowing whom to call in the co-management of difficult orofacial pain, and head and neck pain problems. Orofacial pain programs are important in building greater interaction between Dentistry and Medicine. The general dental education programs will also benefit greatly from the greater availability of trained dentists in this field. Overall, the field of Orofacial Pain is a mosaic, with the existing specialties already playing a focused part of access to care for patients with these conditions. The Boards of the dental specialties are not set up nor require examination of Orofacial Pain to clinical competency as it relates to the primary discipline. The expertise contained within Orofacial Pain programs are complementary to and helpful to the existing accredited specialties and the general dental school clinics. Therefore, the Orofacial Pain program is complementary, and not competitive with existing specialties and their 77 programs, and helpful to , for example, the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery programs just as is the cardiologist to the cardiac surgeon or the orthodontist to oral and maxillofacial surgery. The restorative or occlusal-related disciplines do not take on the care of orofacial pain because the scientific relationship of orofacial pain to dental occlusal problems explain. Guidelines for teaching the comprehensive control of pain and anxiety in dentistry. The specialty applicant must document scientifically, by valid and reliable statistical evidence/studies, that it: (a) actively contributes to new knowledge in the field; (b) actively contributes to professional education; (c) actively contributes to research needs of the profession; and (d) provides oral health services in the field of study for the public; each which the specialty applicant must demonstrate would not be satisfactorily met except for the contributions of the specialty applicant. Cite peer reviewed epidemiological data that establishes the incidence and/or prevalence of conditions diagnosed and/or treated by practitioners in the proposed specialty. According to the most conservative and reliable data on lifetime prevalence and treatment need studies, suggest that 25% to 35% of the population have a current orofacial pain problem that is severe enough to warrant treatment (Table 9) (5-19). Of these we estimate the number of new cases to be at a minimum of about 5-7% of the population. Chronic pain of all types remain one of the great unsolved health problems of this century (1-3). Chronic pain, particularly in the head is the leading cause of disability to workers second only to respiratory infections for lost work days, and by far the leading reason for long term disability. Of these individuals, over 50% of them reported seeking care in the past year for these problems with 50% seeking care for burning mouth, 56% for jaw joint pain, and 61% for facial pain. For example, a 1999 general population survey by Robert Starch Worldwide (4) found that of the 805 individuals who reported having a persistent pain disorder, more than four out of 10 people have yet to find adequate relief, saying their pain is out of control- despite having the pain for more than 5 years and switching doctors at least once. This clearly documents that the treatment by general dentists and specialists is either not provided or inadequate. The results of the previously noted practice survey also found that 89% of dentists would rather refer chronic orofacial pain patients because they are too complex (78%) and not trained(81%). Persistent pain can cause depression, suicidal ideation, dependent relationships, loss of work, disability and many lifestyle disturbances. Based on demographic changes and disease projections, it is estimated that a minimum of 3 million patients with chronic orofacial pain will seek care for their problem this year. Neuropathic and neurovascular disorders that are part of the scope of orofacial pain practice include post-traumatic continuous neuropathic pain, trigeminal neuralgia and pre-trigeminal neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, occipital neuralgia, facial nerve neuralgia, nervus intermedius neuralgia, post-herpetic neuralgia of trigeminal, complex tooth pain from non-dental causes, neurovascular orofacial pain, deafferentation pain syndrome, and sympathetically mediated orofacial pain. Headache can be a symptom of many disorders affecting the orofacial structures and is especially prevalent in patients with orofacial pain disorders.
References:
- https://icmphilly.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Hip-and-Knee.pdf
- https://www.state.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/PEPFAR2019ARC.pdf
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gastroenterology_hepatology/_pdfs/esophagus_stomach/gastroparesis.pdf
- https://www.escardio.org/static-file/Escardio/Medias/associations/acute-cardiovascular-care-association/AcuteCVDays/Acut%20Heart%20Failure%20Chapter%204.pdf
- https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/PDF/rr/rr5905.pdf